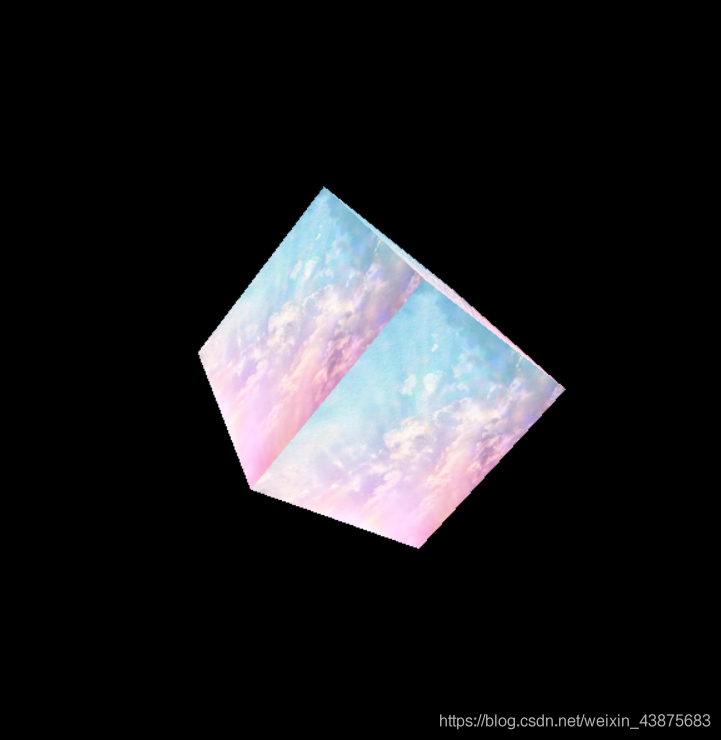
2011-04-15 wcdj
I don’t know why there is no OpenGL header file in SDK after VS2008. Here is a summary for this problem.
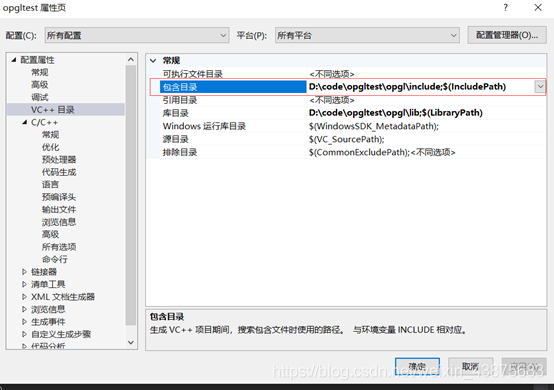
In Lesson 6 of learning Nehe’s texture mapping, I initially needed to use the header file containing gl/glaux. H, but found that I didn’t have this header file on my system. There are two header paths in the compiler that reference OpenGL:
C:/Program Files/Microsoft SDKs/Windows/v6.0 A/include/gl/gl h (the default)
C:/Program Files/Microsoft Visual Studio 9.0/VC/include/gl/glut. H (the new gl manually folder)
Googled the solution.
thod 1: Find the most used solution, but I do not have VS2003 or VS2005 installed on my system, so I cannot copy it.
I have been porting old openGL program to VS2008. I have solved the problem by copying the “include/gl/glaux.h” and “lib/glaux.lib” from the VS2005 Platform SDK located on “C:/Program Files/Microsoft Visual Studio 8/VC/PlatformSDK” To the PlatformSDK of VS2008 located on “C:/Program Files/Microsoft SDKS /Windows/ V6.0a “
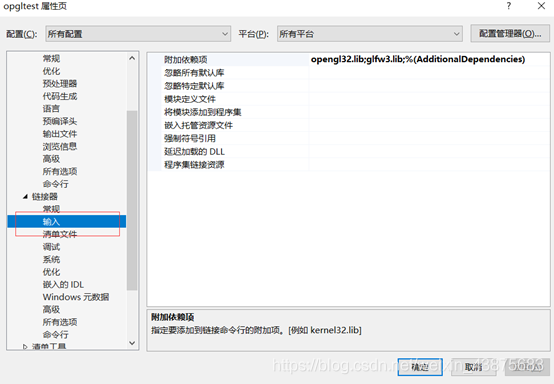
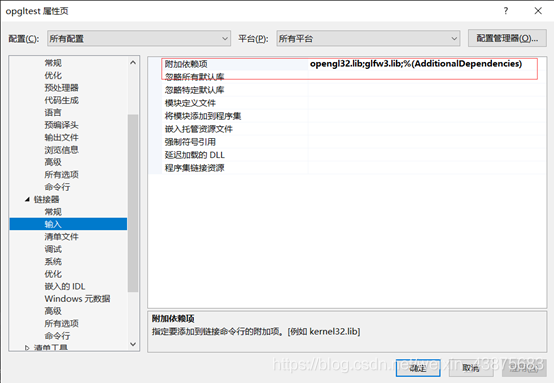
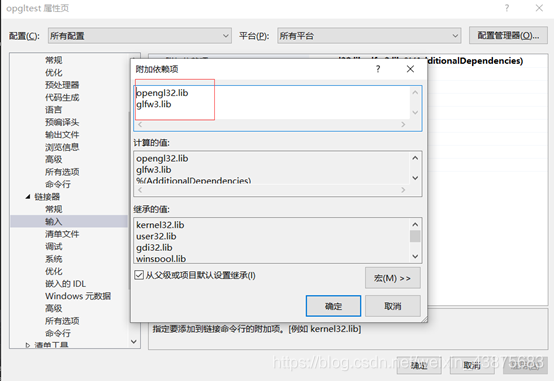
Based on the reply to https://forums.microsoft.com/MSDN/ShowPost.aspx?PostID=1065518& SiteID=1, it looks like glaux. Lib is deprecated. Instead link to kernel32.lib, user32.lib, gdi32.lib and advapi32.lib
The easiest way to sort this out is to:
) Install Glut3.6 or newer as directed.
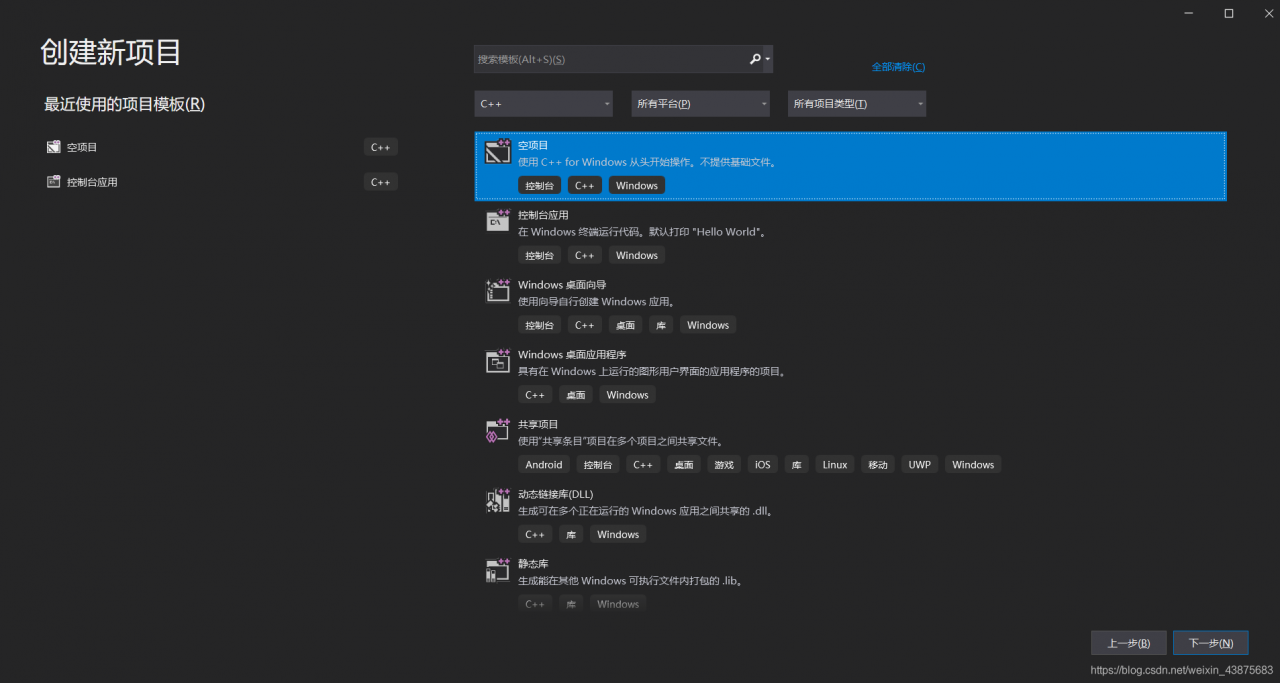
2>pen Visual Studio 2008 and create a new project
3) Cho>C ++ -Empty solution
4) Import Al> the files from your previous OpenGL project
5) delete all headers i.e.
#include < gl/glu.h>
#include < gl/gluax.h>
and any other GL headers
6) then replace with #include < gl/glut.h>
7) recompile.
this worked for all of my 2003 & 2005 Solutions.
thod 4: Download Missing Files.
1: download the source CSDN download
OpenGL installation package download required documents:
http://d.download.csdn.net/down/2560229/ssagnn23 include:
GL. H GLAUX. H GLU. H glut.
H GLAUX. LIB GLU32. LIB glut32. LIB glut. LIB OPENGL32. LIB
GLAUX. DLL GLU32. DLL glut32. DLL glut. DLL OPENGL32. DLL
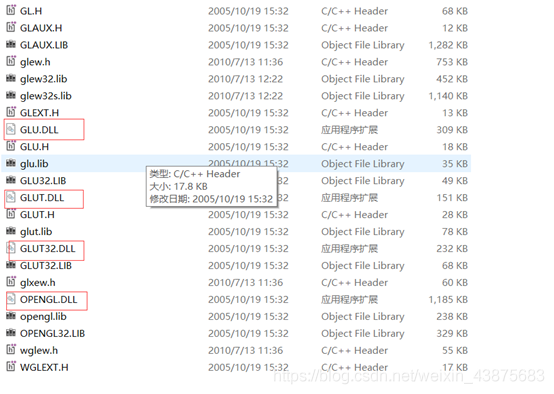
VS2008 without GL. H, H, glu.h, GLAUX. Lib, glu32.lib, opengl32.lib.
1) Copy GLUX. DLL, GLUT32.DLL, GLU32.DLL and GLU32.DLL to C:/WINDOWS/system32, which should already have OpenGL32.DLL and GLU32.DLL.
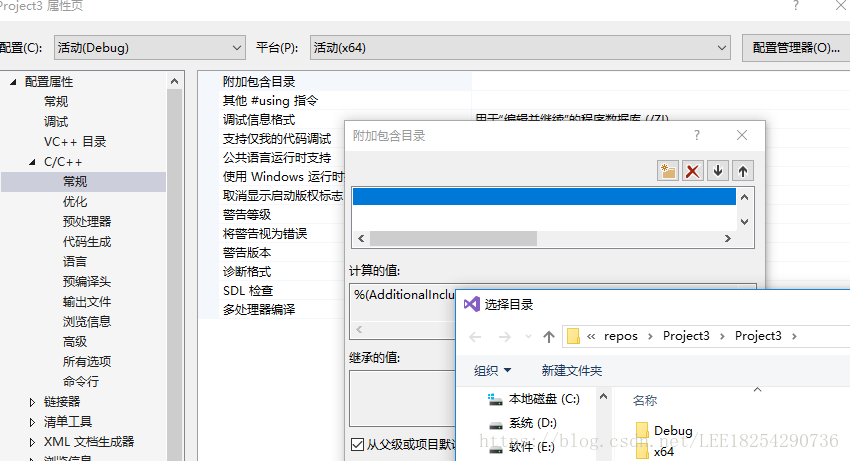
. (2) the GL H, GLAUX. J H, glu. H, glut. H a copy to the C:/Program Files/Microsoft Visual Studio 9.0/VC/include/GL
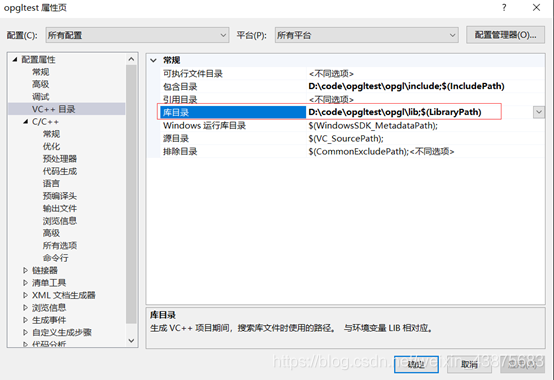
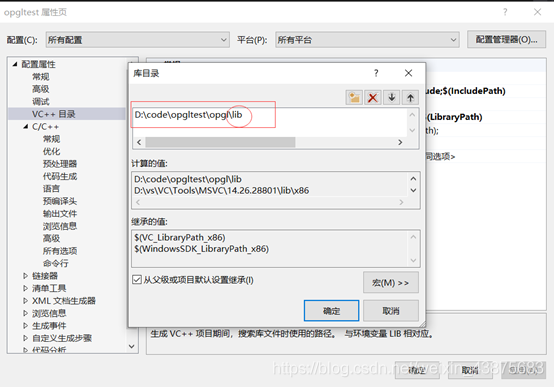
. (3) the GLAUX LIB and Glu32. LIB, glut32. LIB, Opengl32. LIB, C:/Program Files/Microsoft Visual Studio 9.0/VC/lib
br>>
nehe SRC – cn – nehe OpenGL tutorials Chinese version and the code download
http://code.google.com/p/nehe-src-cn/downloads/list nehe OpenGL tutorial Chinese version and the code download
http://www.yakergong.com/nehe/ provides each Lesson # sample code and the file you need.
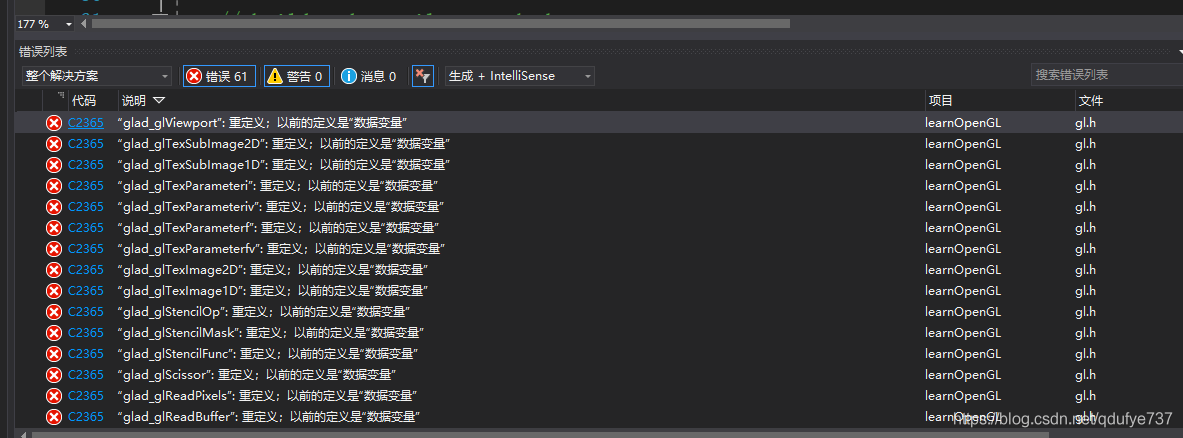
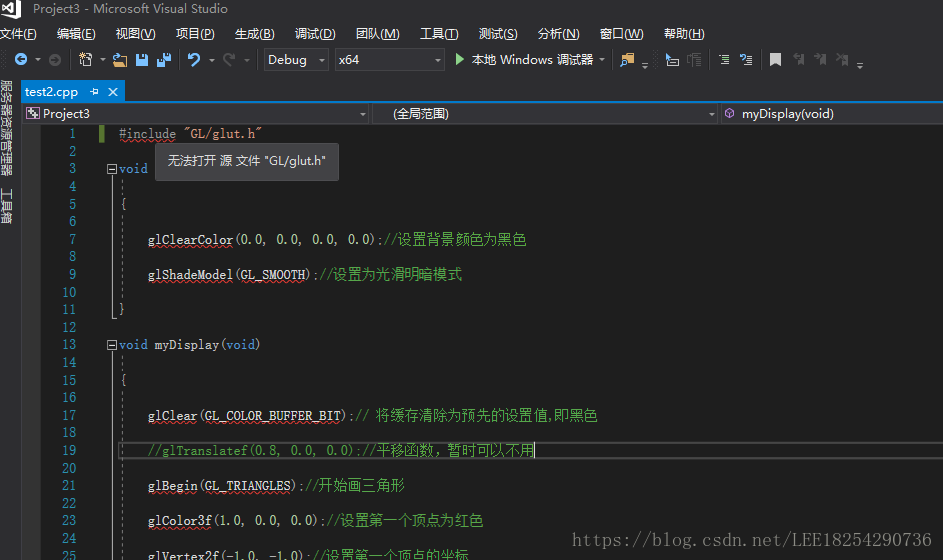
4 according to the method, after downloading the file and configure, recompile, without the previous mistakes, documents found, but the following mistakes.
error C2664: “auxdibimageLoadw” : Cannot convert parameter 1 from “char *” to “LPCWSTR”
is is because I am building a Unicode character set based project, so I want to use wide characters. It is also possible not to use Unicode character sets in the property page ->; Configure properties ->; You can modify it in general. Select not to use the Unicode character set here; that is, select Unset. And then recompile it. OK!
br>>
reference:
missing glaux. H in v6.0 a SDK?
http://social.msdn.microsoft.com/Forums/en/windowssdk/thread/b66e5f7a-91f6-4dbe-b388-0c131008b08f project under VS2003 under VS2008 compilation, however, Can’t find the gl/glaux. H
http://topic.csdn.net/u/20070930/15/6a900f21-8e41-4325-862f-f6df3a425f36.html VS 2008 OpenGL configuration
http://lujun5918.blog.163.com/blog/static/287227712011013114410553/ Load images generated texture opengl program
http://topic.csdn.net/u/20070823/19/4497cb18-be2a-464f-ad20-b12191a61b26.html
 64 choose
64 choose 



 b5
b5 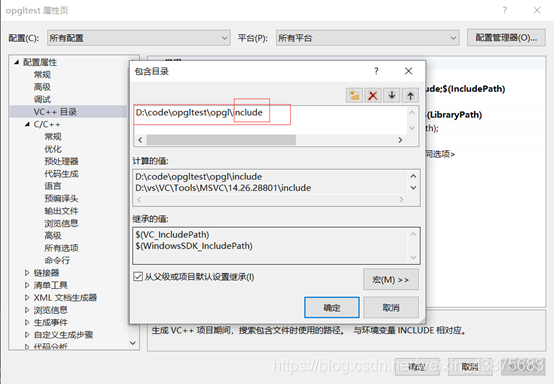
 <>bb4
<>bb4 