Blending can make the object transparent.
Transparency can be achieved in two ways:
‘1’ means discard part of the fragments. In this case, there are no translucent fragments.
Two is really mixing. The current segment and the target segment are weighted according to a certain formula.
【 1 】
#version 330 core
out vec4 FragColor;
in vec2 TexCoords;
uniform sampler2D texture1;
void main()
{
vec4 texColor = texture(texture1, TexCoords);
if(texColor.a < 0.1)
discard;
FragColor = texColor;
}A segment that is always bright, discarded, but this if will branch logically, so that’s the efficiency…
Set the surround texture to GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE to slightly improve the visual effect.
[2] Mixing
Enable the blend: glEnable(GL_BLEND);
GLBLENDFUNC (GL_SRC_ALPHA, GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA);
So source alpha and 1-source alpha
Here glblendFunc is the mixed operation setup function.
GlblendFunction Separate is a bit more subtle and allows you to set the action function for both color and Alpha separately.
Both set the source and target, how to handle RGB and alpha values.
GlblEndequation can be used to set the blending operator. In fact, the most common one is GL_FUNC_ADD
This function sets the formula to use to handle the alpha and RGB values.
The principle of mixing:
If you’ve already drawn something before mixing it (even a skybox is OK), what about wool?
When blending, the object to be drawn is the Source, and the object already drawn is the Target.
When blending, you don’t have to change anything in your Shader. The pieces will blend themselves with the drawn pieces according to the blending formula and numerical rules. Unity uses the syntax of ShaderLab to set up these functions.
An explanation of a previously encountered problem:
A few months ago, I had an issue with WorldCreatorPro where the trees would become translucent slices when I used Slice LOD instead of SpeedTree, which was far away from the map. At this point, the translucent area hides the terrain behind.
Now it’s easy to explain. Borrowing the graph from the Learnopengl author:
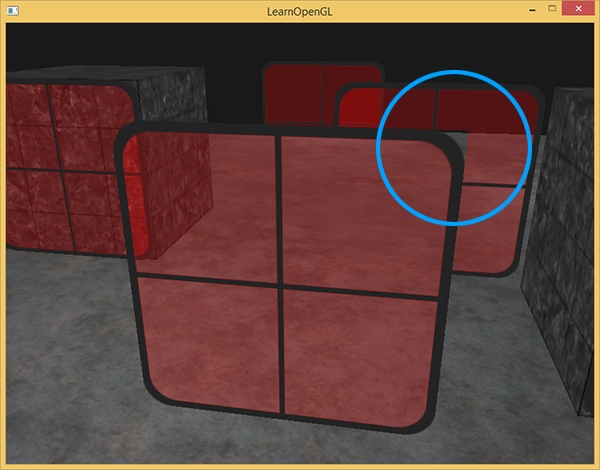
Look at the hoop:
If the previous diagram is drawn first, the transparent pixels here will also be written to the ZBuffer, since the Z-Buffer ignores Alpha.
When the object behind is drawn (whether it is transparent or not, as long as it is farther away from the object in front) the z-test fails and the corresponding pixel is discarded.
Conclusion: When Z-buffer and Blending theory are used together, it is necessary to draw distant objects first and then close ones to ensure no mistakes.
The trees we used before, even if we could sort them, it would be a terrible overhead to arrange thousands of trees in order every frame and then render them. So we could just switch to SpeedTree and use model LOD instead of map LOD, although it would be really cheap.
Method: How to use Blending correctly.
- Draw all opaque objects first. Sort all transparent objects. Draw all transparent objects in order (from far forward). In particular, you can sort by distance insertion, drawing far away first, and then drawing near.