1. Principle
Synchronized thread synchronization
Notify() calls up the thread
The wait() thread waits
2. Code examples
package com.thread;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class TasksTestSync extends Thread {
private static Integer num = 0;
private int id;
public TasksTestSync(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (num < 12) {
synchronized (TasksTestSync.class) {
num = num + 1;
System.out.println("thread_" + id + " num:" + num);
TasksTestSync.class.notify();
try {
TasksTestSync.class.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread0 = new TasksTestSync(0);
Thread thread1 = new TasksTestSync(1);
ExecutorService exec = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
exec.submit(thread0);
exec.submit(thread1);
exec.shutdown();
}
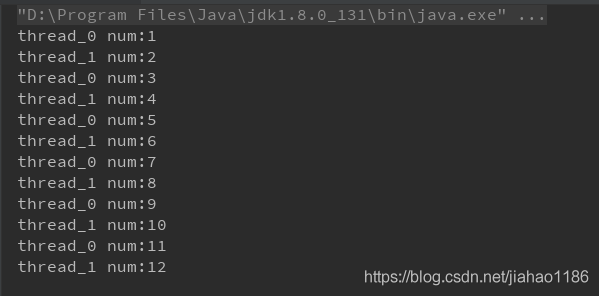
}3. Implementation results