Solution:
kubeadm join Add note error:[ERROR FileExisting-conntrack]: conntrack not found in system path, execute yum install -y conntrack and then re-execute command: kubeadm join
Done!
Solution:
kubeadm join Add note error:[ERROR FileExisting-conntrack]: conntrack not found in system path, execute yum install -y conntrack and then re-execute command: kubeadm join
Done!
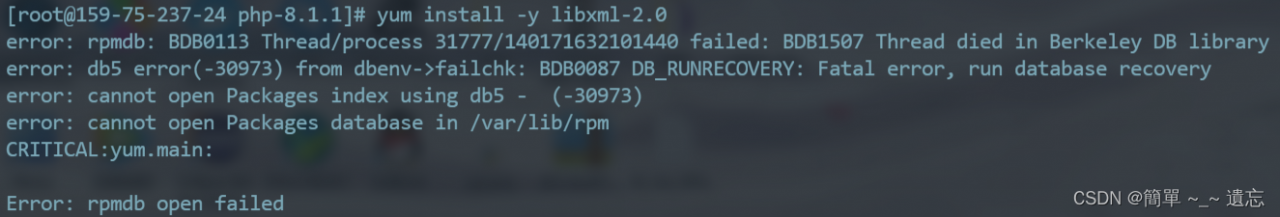
When installing dependencies using Yum in CentOS, the following errors are reported:
the solution is as follows:
Execute the following commands in order
# Go to the directory where rpmdb is located
cd /var/lib/rpm
# Clear the original rpmdb file
rm -f __db.*
# Rebuild the rpm database
rpm --rebuilddb
# Clear all yum caches
yum clean all
After execution, use Yum to install the dependent packages normally
Yum to install the package and prompt the error “error: rpmdb open failed”.
Solution:
rpm --rebuilddbCause: build lamp environment, linux environment is centos6 64 bit, run the instruction “Yum remove httpd” to remove the original Apache
Complete error prompt:
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, refresh-packagekit, security
Setting up Remove Process
Resolving Dependencies
--> Running transaction check
---> Package httpd.i686 0:2.2.15-29.el6.centos will be erased
--> Processing Dependency: httpd >= 2.2.0 for package: gnome-user-share-2.28.2-3.el6.i686
--> Running transaction check
---> Package gnome-user-share.i686 0:2.28.2-3.el6 will be erased
--> Finished Dependency Resolution
YumRepo Error: All mirror URLs are not using ftp, http[s] or file.
Eg. Invalid release/repo/arch combination/
removing mirrorlist with no valid mirrors: /var/cache/yum/i386/6/base/mirrorlist.txt
Error: Cannot retrieve repository metadata (repomd.xml) for repository: base. Please verify its path and try again
You could try using --skip-broken to work around the problem
You could try running: rpm -Va --nofiles --nodigest
terms of settlement:
Just run the following three instructions
ed -i "s|enabled=1|enabled=0|g" /etc/yum/pluginconf.d/fastestmirror.conf
mv /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo.backup
curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo https://www.xmpan.com/Centos-6-Vault-Aliyun.repo
There is another solution in the original, but I solved it with the first one. If you can’t solve it with this method, you can try the second one in the original https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_ 45621658/article/details/110734514
Loaded plug-ins: fastestmirror
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
One of the configured repositories failed (none),
and yum doesn’t have enough cached data to continue. At this point the only
safe thing yum can do is fail. There are a few ways to work “fix” this:
1. Contact the upstream for the repository and get them to fix the problem.
2. Reconfigure the baseurl/etc. for the repository, to point to a working
upstream. This is most often useful if you are using a newer
distribution release than is supported by the repository (and the
packages for the previous distribution release still work).
3. Run the command with the repository temporarily disabled
yum --disablerepo=<repoid> ...
4. Disable the repository permanently, so yum won't use it by default. Yum
will then just ignore the repository until you permanently enable it
again or use --enablerepo for temporary usage:
yum-config-manager --disable <repoid>
or
subscription-manager repos --disable=<repoid>
5. Configure the failing repository to be skipped, if it is unavailable.
Note that yum will try to contact the repo. when it runs most commands,
so will have to try and fail each time (and thus. yum will be be much
slower). If it is a very temporary problem though, this is often a nice
compromise:
yum-config-manager --save --setopt=<repoid>.skip_if_unavailable=true
Cannot retrieve metalink for repository: epel/x86_64. Please verify its path and try again
Follow the prompts to correct the source.
cd /etc/yum.repos.d
vi epel.repo
The revised contents are as follows:
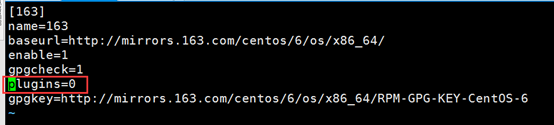
[epel]
name=Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux 7 - $basearch
baseurl=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/epel/7/$basearch
#metalink=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/metalink?repo=epel-7&arch=$basearch
failovermethod=priority
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-EPEL-7
[epel-debuginfo]
name=Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux 7 - $basearch - Debug
baseurl=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/epel/7/$basearch/debug
#metalink=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/metalink?repo=epel-debug-7&arch=$basearch
failovermethod=priority
enabled=0
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-EPEL-7
gpgcheck=1
[epel-source]
name=Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux 7 - $basearch - Source
baseurl=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/epel/7/SRPMS
#metalink=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/metalink?repo=epel-source-7&arch=$basearch
failovermethod=priority
enabled=0
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-EPEL-7
gpgcheck=1
Execute the following command:
yum clean all
yum makecache
yum update
yum install -y git
Yum installation and use returned to normal.
All mirror URLs are not using ftp, http[s] or file
Because the support of centos6 has been officially stopped
To solve this problem, execute the following command:
sed -i "s|enabled=1|enabled=0|g" /etc/yum/pluginconf.d/fastestmirror.conf
mv /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo.backup
curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo https://www.xmpan.com/Centos-6-Vault-Aliyun.repo
yum clean all
yum makecacheIt’s OK
Question:
Installing and downloading graphical interface Gnome
Yum groupinstall “desktop”
Yum groupinstall “X window system”
Yum groupinstall “Chinese support” (optional)
The screenshot of the later error is as follows: 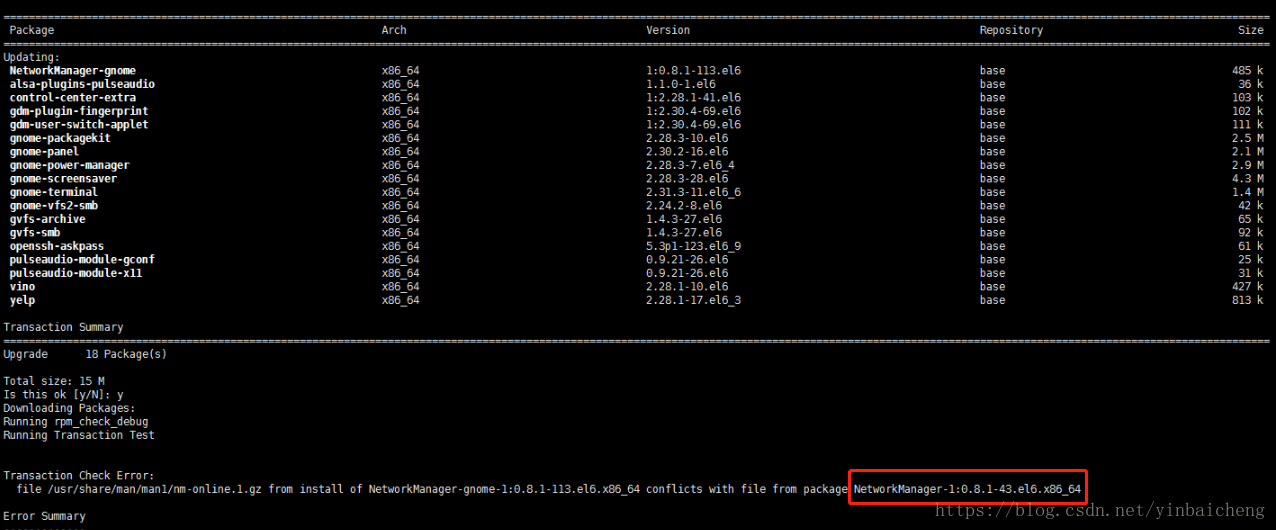
resolvent:
Use the command: Yum remove networkmanager-1: 0.8.1-43.el6.x86_ 64 first delete the conflicting package shown in the red box in the above screenshot.
[fedora]
name=Fedora $releasever - $basearch
failovermethod=priority
baseurl=http://archives.fedoraproject.org/pub/archive/fedora/linux/releases/$releasever/Everything/$basearch/os/
#mirrorlist=https://mirrors.fedoraproject.org/metalink?repo=fedora-$releasever&arch=$basearch
enabled=1
metadata_expire=7d
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-fedora-$basearch
[fedora-debuginfo]
name=Fedora $releasever - $basearch - Debug
failovermethod=priority
baseurl=http://archives.fedoraproject.org/pub/archive/fedora/linux/releases/$releasever/Everything/$basearch/debug/
#mirrorlist=https://mirrors.fedoraproject.org/metalink?repo=fedora-debug-$releasever&arch=$basearch
enabled=0
metadata_expire=7d
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-fedora-$basearch
[fedora-source]
name=Fedora $releasever - Source
failovermethod=priority
baseurl=http://archives.fedoraproject.org/pub/archive/fedora/linux/releases/$releasever/Everything/source/SRPMS/
#mirrorlist=https://mirrors.fedoraproject.org/metalink?repo=fedora-source-$releasever&arch=$basearch
enabled=0
metadata_expire=7d
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-fedora-$basearchThen you can install the software normally
.
plus those two parameters mean that
is installed without having to dependencies among packets, and
does not count error: Failed dependencies: such errors
In RedHat Linux and Other RedHat compliant distributions such as Mandrake, the entire distribution is installed using RPM. So the best way to install new software is to
downloading RPM packages from the network.
1) to install a package using an RPM, the simplest command is as follows:
# rb-ivh foo-1.0l-l.is386.rpm (the package in question is foo-1.0l-l.is386.rpm, all of the following)
foo#################### ############. Installation is simple.
2) remove installed packages
to uninstall package foo, simply enter the following command:
# rpm-e foo
note: the package name is foo, not the RPM file name “foo-1.01-l.b.i. 386.rpm”.
3) upgrading packages to upgrade the software is similar to install the software:
# RPM – Uvh foo – 2.0 – l.i 386 RPM
foo# # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # #
user note: RPM will automatically install the old version of the corresponding software package. Rpmsave
saving /etc/foo.conf as /etc/foo.conf.rpmsave
so that the user can manually change the configuration file. In addition, if the user wants to install the older version of the software, the user will see the following error message:
# rpm-uvh foo-1.0-l.i386. RPM
foo packag foo-2.0-l(which is newer) is already installed
error: foo-1.0l-l.i 386. RPM cannot be installed
.
user can use rpm-q to query the corresponding software in the RPM database, RPM will give the name of the software package, version, release version number, for example:
# rpm-q foo
foo-2.0-l
the following is the query can use the specific parameters:
-a query the current system installed all software packages.
-f filename query includes ga file packages.
– F with the -f parameter, just input is standard input (for example the find/usr/bin | RPM – qF)
– q package name:
– q query the package with the -p parameter, just input is standard input (for example the find/MNT/cdrom/RedHat/RPMS | RPM – qQ)
here is the format of the output options:
– I displays the name of the package, description, distribution, size, date of compilation, the date of installation, developers and other information.
-l display the files contained in the software package
-s display the current status of the files contained in the software package, only two states: normal and missing
-d display the documents in the software package (such as man,info,README, etc.)
-c display the configuration files in the software package, these files generally need to be manually modified by the user after installation, for example: Sendmail. Cf, passwd, inittab etc.
if using the -v parameter can be similar to the output of the ls -l
5) in the RPM packages
users can use the RPM used to check the package has been installed, the RPM can check file size, MD5 check code, file permissions, type, and the information such as owner.
here is the parameter description:
– a simple calibration software package if the file exists
– b check package in a single file
– c check installation of all packages – d compare a source package and already installed packages
if the test through, there is no any error messages, if there is an error message, its format is as follows: the error information is one of the eight string, if it is a “. “, means there is no problem, here is the meaning of the corresponding characters: MD5 check error
5 MD5 check error
S file size error
L symbolic connection
T file modification time error
D device file error
U user name error
G group name error
M attributes (including overwrite weight and file type) error
if the user sees this information, it is best to reinstall or manually repair.
+ + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + +
+ + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + +
the RPM practical skills!
1) users can install packages via FTP. If users will be able to connect on the network, want to install a new software package, you can directly use it to install to the URL:
for example: under ftp.linuxsir.com/pub/linux/redhat/RPMS/ now have this file package: foo – 1.0-1. I386 RPM, then you can use this command:
# RPM -i ftp.linuxsir.com/pub/linux/redhat/RPMS/foo-1.0-1.i386.rpm
to install, also can query!
2) if the user accidentally wushan several files, but not sure whether those documents, want to check to the whole system, in order to understand which parts may be damaged, you can use:
# RPM – Va
3) if the user meets a person not to come out of the file, want to know it belongs to the words of a software package, you can do it:
# rpb-qf /usr/X11R6/bin/xjewel
results are obtained with the following information:
xjewel-1.6-1
4) if the user gets a new RPM file, but does not know its contents; Or to find out which files a particular file package will install on your system, do this:
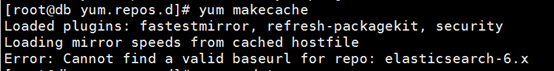
[root@db yum.repos.d]# yum makecache
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, refresh-packagekit, security
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
Error: Cannot find a valid baseurl for repo: elasticsearch-6.x
[root@db yum.repos.d]# vim /etc/yum/pluginconf.d/fastestmirror.conf
Change 1 to 0
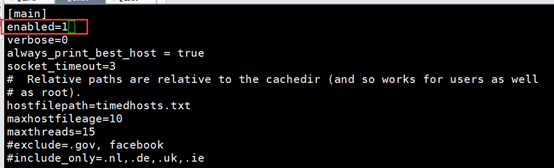
Then go to the yum source and configure
If there are plugins=1 then change it to 0, not adding them.