Record it! After half a month of internship, when I changed the bug today (an interface for modifying personal information), it was obviously changed, and the test environment was running smoothly. When I opened the test environment demonstration, I click submit to modify and report an error network error as shown in the following figure

I opened F12 to view the request, and found that the status was CORS error. My first feeling was that there was a cross domain problem, but I should not, Just opened the console and reported an error, as shown in the figure below:
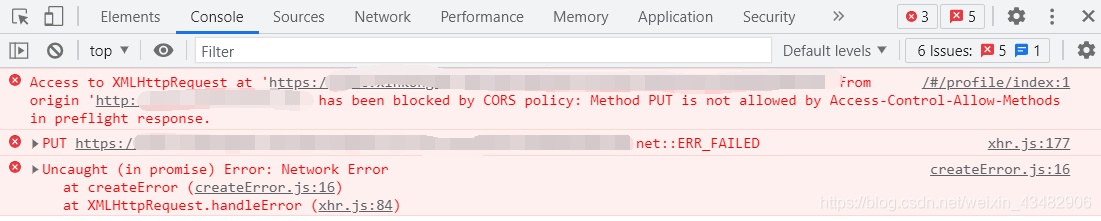
I still feel that it is cross domain, but it should not be cross domain ~
finally, I found that the top left corner of the browser is as shown in the figure
![]()
remember that the company’s domain name has a certificate, is it because there is no s, so I changed the address bar HTTP to HTTPS, The problem is solved ~
then the cross domain reason should be that http//: test.xxx.com visited the interface of HTTPS: test.xxx.com, while the domain name allowed to cross domain in the background is http//: test.xxx.com https://test.xxx.com , which leads to cross domain ~
lack of talent and learning, misunderstanding and mistakes, please give us some advice in the comments area~
Tag Archives: Cross domain problem of Ajax
[Solved] Access to XMLHttpRequest at ‘http://127.0.0.1:5000/markdownlang/‘ from origin ‘null‘ has been bl
When AJAX is used, the above cross domain request error is reported (using Python flash to build the background)
Error code:
from flask import Flask,render_template
@app.route("/markdownlang/",methods=["post"])
def getMarkdownLang():
return render_template('result.html')
Solution: add a response header on the server side to simply allow cross source.
from flask import Flask,render_template,make_response
@app.route("/markdownlang/",methods=["post"])
def getMarkdownLang():
resp = make_response(render_template('result.html'))
resp.headers['Access-Control-Allow-Origin'] = '*'
return resp
There are two other things that can go wrong:
-
- the requested path is not complete. Full path http://127.0.0.1:port number/file path. Cross source must have full path. The request mode has no corresponding response code on the server side. For example, the server should have a post response for a post request
Spring boot uses configuration interface webmvcconfigurer to solve cross domain problems
1. Problem Description: cross domain problem in front end call interface
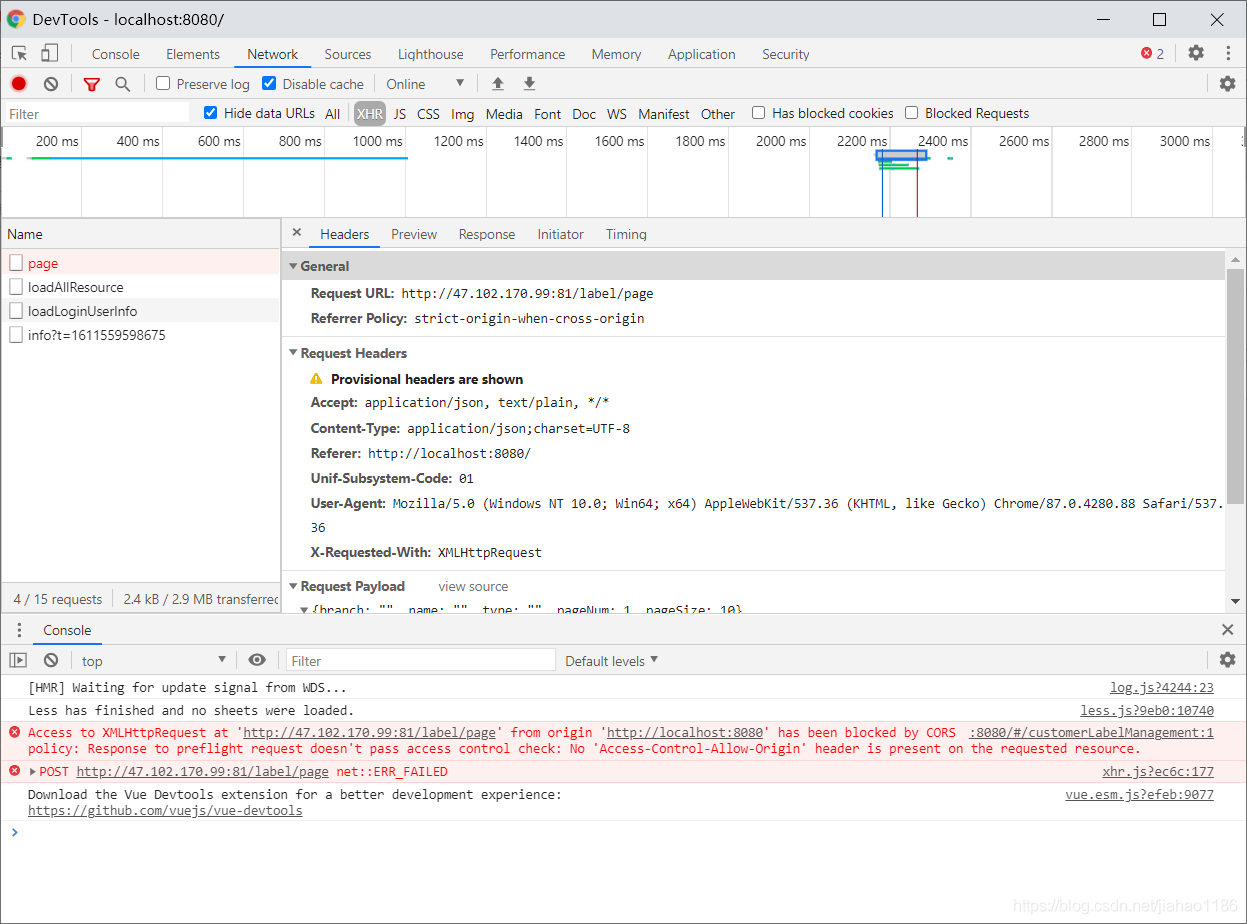
2. Solution, add the following classes
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.CorsRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
public class CorsConfiguration {
@Bean
public WebMvcConfigurer corsConfigurer() {
return new WebMvcConfigurer() {
@Override
public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
registry.addMapping("/**")
.allowCredentials(true)
.allowedMethods("POST", "GET", "PUT", "OPTIONS", "DELETE")
.allowedOrigins("*");
}
};
}
}
The 1) Attribute value, origins: configure the sources that can be accessed, for example: 0 https://adong.blog.csdn.net/article/details/113126033 2) Property methods: configure the methods of cross domain request support, such as get, post, delete, put, and return all supported methods at one time. 3) Attribute maxage: configures the valid time of the pre check request. The unit is seconds. It indicates how long the second pre check request does not need to be issued. 4) Attribute allowcredentials: configure whether to allow sending cookies for credential requests. Cookies are not sent by default. 5) Attribute allowedheaders: configure the allowed custom request headers for pre checking requests. 6) Attribute exposedheaders: configure the header information of the response, in which other header information can be set. Without configuration, cache control, content language, content type, expires, last modified and pragma fields can be obtained by default.
> access control allow- Credentials
allowedheads
string array
class or interface
no
access control request heads
Note:
exposed heads
string array
class or interface
no
access control expose heads
* indicates that all domain names are allowed.