RPC: Remote process call:
Several more typical RPC implementation and invocation frameworks (note: not a development framework) :
1: RMI: Implemented using the Java.RMI package, based on Java remote Method protocol and native Java serialization implementation.
2: hession: altogether lightweight remoting onhttp tool that provides RMI functionality with a simple approach based onhttp protocol.
3: Thrift: Thrift is a framework for scalable cross-language services.
Implementation principle of RPC framework:
There are three main roles in the framework, provider, Consumer, and Registry.
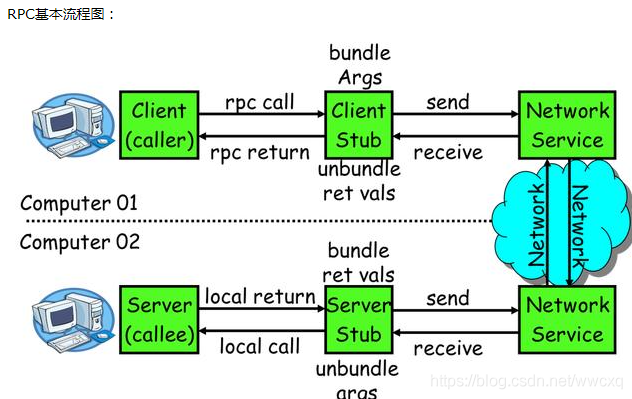
The techniques used in RPC:
1: Dynamic proxy: Java dynamic proxy technology is required to generate Client stub and Server stub. You can use the JDK’s native dynamic proxy mechanism. You can also use open source bytecode tools such as Cglib, Javassist.
2: Serialization: To be able to transfer and receive Java objects over the network, serialization and deserialization operations are required. Serialization is the process of converting Java objects to Byte [], and thus encoding. Deserialization is the process of converting a Byte [] into a Java object, or decoding. Java’s native serialization mechanism is available but inefficient, and it is recommended to use open source mature serialization technologies such as Protobuf, Thrift, and Hessian.
Nio: Many RPC frameworks use netty directly.
Service Registry: Redis, ZK, Elling, EtCD
Several more typical RPC implementation and invocation frameworks (note: not a development framework) :
1: RMI: Implemented using the Java.RMI package, based on Java remote Method protocol and native Java serialization implementation.
2: hession: altogether lightweight remoting onhttp tool that provides RMI functionality with a simple approach based onhttp protocol.
3: Thrift: Thrift is a framework for scalable cross-language services.
Implementation principle of RPC framework:
There are three main roles in the framework, provider, Consumer, and Registry.

The techniques used in RPC:
1: Dynamic proxy: Java dynamic proxy technology is required to generate Client stub and Server stub. You can use the JDK’s native dynamic proxy mechanism. You can also use open source bytecode tools such as Cglib, Javassist.
2: Serialization: To be able to transfer and receive Java objects over the network, serialization and deserialization operations are required. Serialization is the process of converting Java objects to Byte [], and thus encoding. Deserialization is the process of converting a Byte [] into a Java object, or decoding. Java’s native serialization mechanism is available but inefficient, and it is recommended to use open source mature serialization technologies such as Protobuf, Thrift, and Hessian.
Nio: Many RPC frameworks use netty directly.
Service Registry: Redis, ZK, Elling, EtCD