1. Principle and mechanism
Use one-way pool to ensure orderly submission and execution.
explain:
1) Alternate execution between threads is not supported.
2) Multithreading is not synchronous, only to ensure the order of execution, multithreading is concurrent execution.
2. Code examples
package com.thread;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class TasksWithoutLockTest extends Thread {
private static int num = 0;
private int id;
public TasksWithoutLockTest(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Thread" + id + "output num:" + num++);
try {
Thread.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//ExecutorService exec = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
ExecutorService exec = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor();
for (int i = 0; i < 12; i++) {
exec.submit(new TasksWithoutLockTest(i));
}
exec.shutdown();
}
}3. Output results
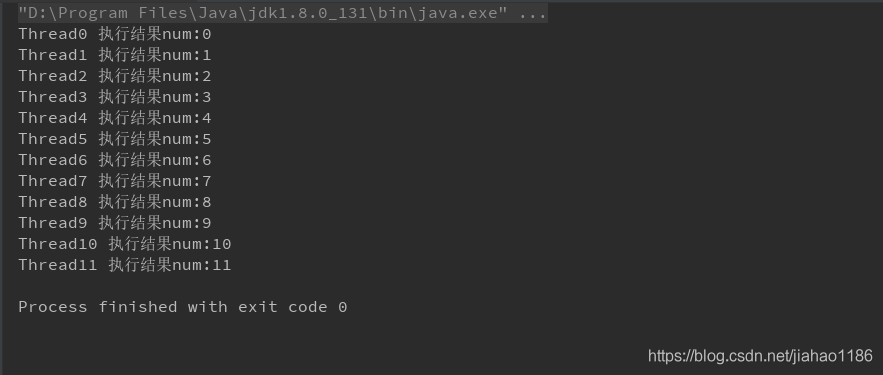
Read More:
- Three ways of thread sequence alternate execution in Java lock free programming
- Spring boot uses thread pool to realize asynchronous processing without return and asynchronous processing with return
- [Solved] Spring integrates canal to call feign error: pool-1-thread-1
- The thread implementation of timer in Java
- Java uses class array to report error Exception in thread “main” java.lang.NullPointerException solution
- Jmeter Error: ERROR o.a.j.JMeter: Uncaught exception in thread Thread[AWT-EventQueue-0,6,main]
- [Solved] Docker Elasticsearch8.4.0 Error: Exception in thread “main” java.nio.file.FileSystemException
- [Solved] qrcode-error: Exception in thread “main” java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError…
- [Solved] Exception in thread “main“ java.lang.NoSuchFieldError: level
- Non empty judgment method: the difference between isnotempty and isnotblank. isNullOrEmpty
- Flink Error: is not serializable. The object probably contains or references non serializable fields.
- [Solved] Hadoop Error: Exception in thread “main“ java.io.IOException: Error opening job jar: /usr/local/hadoop-2.
- Mybatis query error: Exception in thread “main” org.apache.ibatis.exceptions.PersistenceException…
- Mapper.xml Error: Error setting non null for parameter #3 with JdbcType null.
- [Solved] Error: A JNI error has occurred, please check your installation and try again Exception in thread
- [PROJECT] itdage java to get the weather and send text messages
- Java database Druid error: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource error
- JAVA 8: How to Convert List to Map
- Asynchronous callback case of Java callback function
- The number of control threads and concurrency number of concurrent executor of Java starting gun