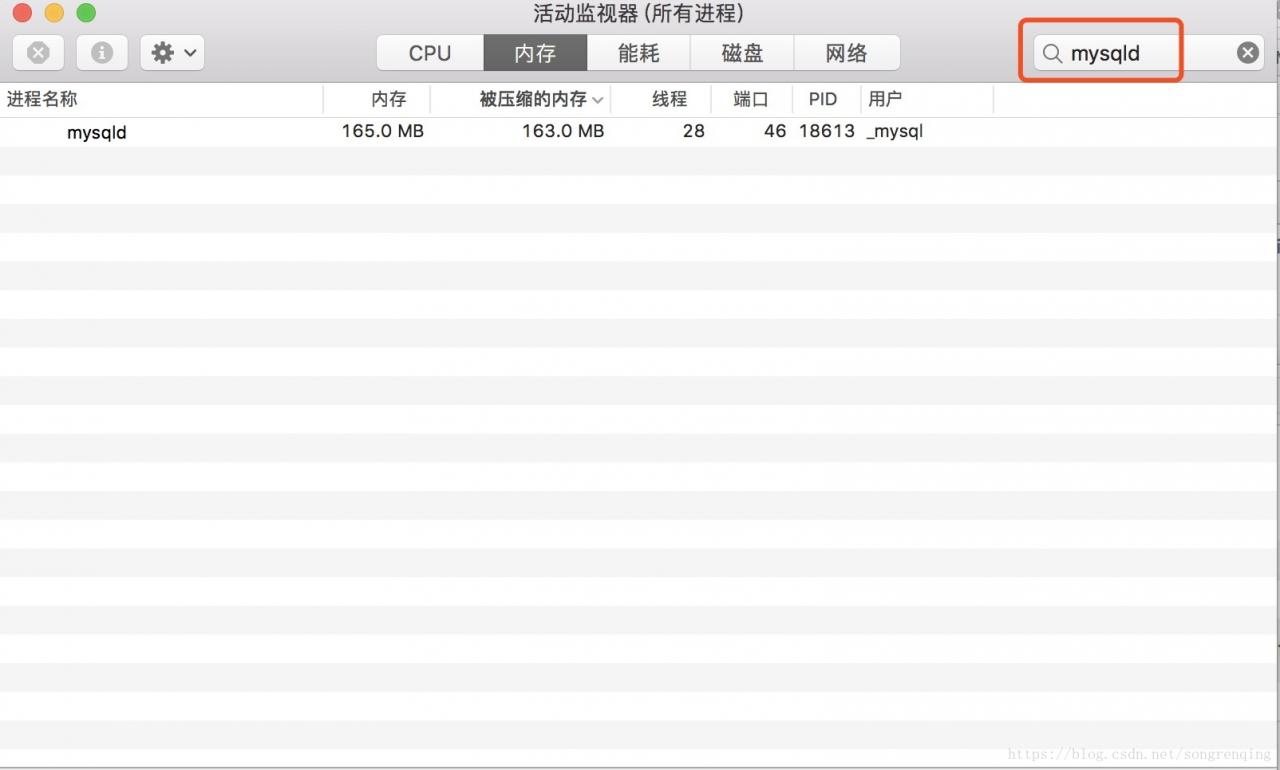
Error 1045(28000) Access Denied for user ‘root’@’localhost’
From http://zxy5241.spaces.live.com/blog/cns! 7682A3008CFA2BB0! 361.entry
When installing mysql database in Windows operating system, you encounter Error 1045(28000) Access Denied for user ‘root’@’localhost’, you need to reset the password.
the specific method is:
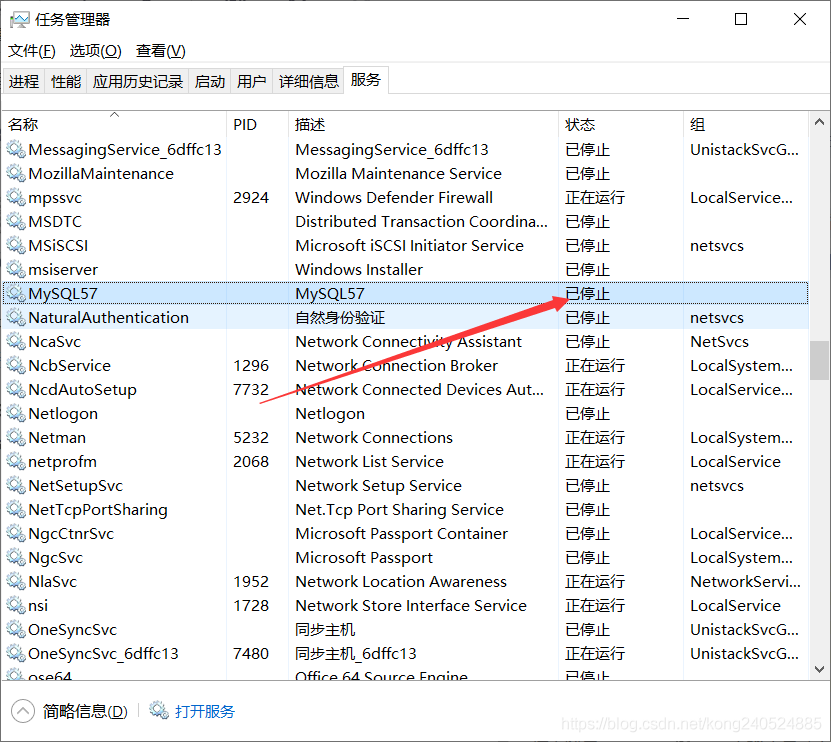
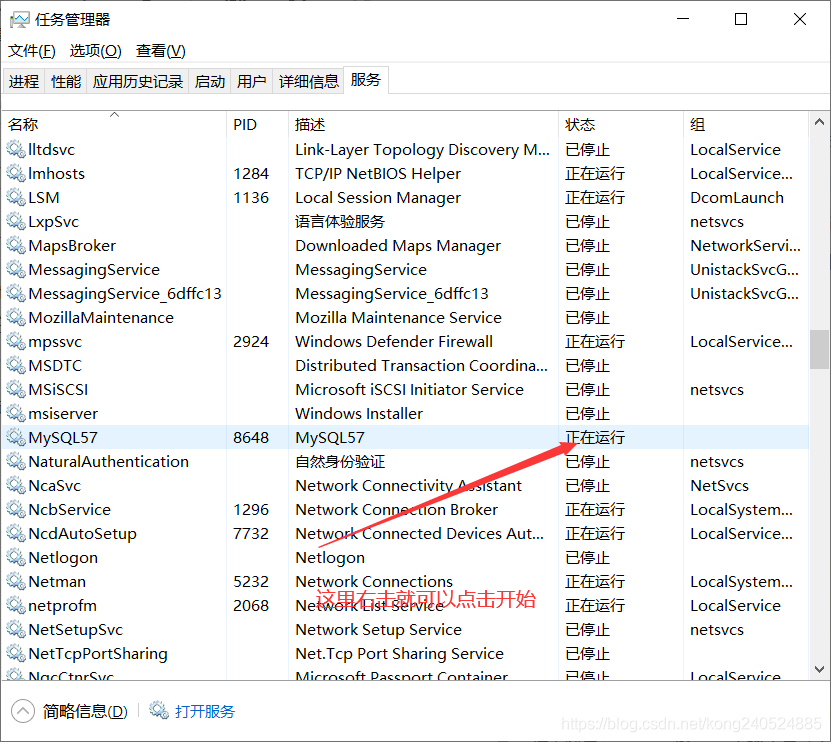
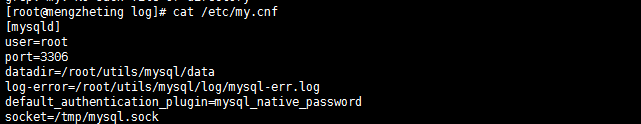
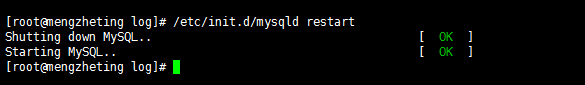
1. First, find my. Ini configuration file in the installation directory, open the configuration file, find the line [mysqld], add skip-gran-tables below and save the file, and restart mysql dynamic service.
2. Then execute mysql -u root mysql
mysql> update user set password=password(‘newpassword’) where user=’root’;
mysql> Flush privileges;
where newpassword is root’s newpassword. 3. Remove the line that added to my. Ini configuration file just now, and finally restart mysql.
After installing mysql or uninstalling the downloaded free version, the default is no my.ini file.
. However, there are several similar files, such as [code] my-small-ini, my-media.ini, my-large. Ini, my-huge. Ini, [/code].
these files are the different configuration information recommended by mysql for different applications; But these configurations will only be applied if you put them in my. Ini.
where:
1, my-small. Ini is designed for small database. This model should not be used for databases that contain common items.
2, my-media.ini is designed for medium-sized databases. If you are using RHEL in the enterprise, you will have significantly more physical memory than the minimum RAM requirements for this operating system (256MB). As you can see, if you have that much RAM memory available, you can naturally run other services on the same machine.
3, my-larg.ini is designed for use exclusively with a SQL database. Since it can use up to 512MB of memory for the database, at least 1GB of RAM will be required on this type of system so that it can handle both operating system and database applications.
4, my-huge. Ini is designed for databases in enterprises. Such a database would require a dedicated server and 1GB or more of RAM. These choices are highly dependent on the amount of memory, the speed of the computer, the size of the database details, the number of users accessing the database, and the number of users loading and accessing data into the database. The performance of the database may change as the number of databases and users increases.
according to their own situation, select a file configuration copy to my. Ini file, of course, you need to create your own, just create a new file, and then copy into the configuration information.