Question.
python lx@lx-PC: ~ $
Can’t find a platform independent library & lt; prefix>
Platform Dependency Library Not Found& lt; exec_prefix>
Consider setting the dollar PYTHONHOME & lt; prefix> [: & lt; exec_prefix>]
python fatal error: Py_Initialize: cannot get region code
ModuleNotFoundError: No module is named “code”.
Similar problems:Commanded conda
The temporary solution is.
export PATH="/home/[your_name]/anaconda/bin:$PATH"
However, after the next restart, this problem will still occur, so we need acivate ~/.bash_profile
. ~/.bash_profile
#or
source ~/.bash_profile
That should get us there.
The first step is to find the Python directory
1. Default Python installation
Normally, Python comes pre-loaded with Linux, but at a lower level, for example, Python2.7.10 is pre-loaded with Ubuntu15.
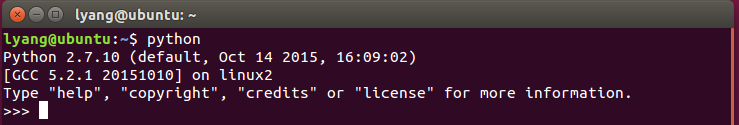
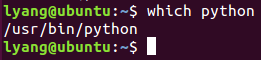
Use the command: which Python to see the current Python installation path:
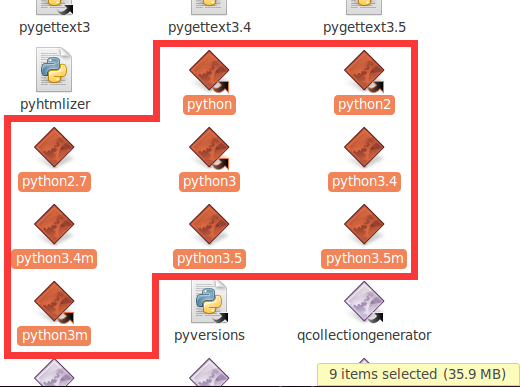
If you open the corresponding path, you can see that the python directory has these files, that is, the directory with similar files (Python, Python 2, Python 2.7) is the corresponding Python directory in your system:
If a version of Python3 is not explicitly required, the 2.7.10 version can be used instead.
It is explicitly required to use Python3 and then make changes.
One thing to note here is that python, Python 2, Python 3 exist in the figure above, which means that versions 2 and 3 are installed,
step 2:
Linux adds the command to PATH:
LinuxApacheBash
Simply put, PATH is a string variable for a set of paths. When you type a command that doesn’t have any paths, LINUX looks for that command in the PATH record. If there is, it will be executed, if there is no prompt command can not be found. For example, in the root directory/can enter the command ls, in the directory /usr can also enter ls, but in fact ls command is not in the two directories, when you enter ls command LINUX will go to /bin,/usr/bin,/sbin and other directories to find the command. PATH is the variable that defines the PATH strength such as /bin:/sbin:/usr/bin, where the colon is the separator between directories.
How to customize path:
if you new compiler installed an apache under/usr/local/apache, every time you want to start not to knock a string of characters (#/usr/local/apache/bin/apachectl start) to use it, but direct anywhere like ls direct input like this (# apachectl start) a brief command. In this case, you need to change the environment variable PATH, or to be more precise, add a value to PATH, /usr/local/apache/bin. There are three ways to add /usr/local/apache/bin to your PATH:
1, directly from the command line setup PATH
# PATH = $PATH:/usr/local/apache/bin
using this method, applies only to the current session, that is to say, whenever logout or cancellation of system, the PATH Settings will be failure.
2, set in the profile PATH
# vi/etc/profile
find export line, a new line below, content is: the export PATH = $PATH:/usr/local/apache/bin.
note: = no Spaces on either side of the equal sign. This is the best approach, and will not change unless you manually force the PATH value to change.
the change to PATH does not take effect immediately after you edit /etc/profile. If you want to take effect immediately, you can execute the # source profile command.
3, in the current user profile set PATH
# vi ~ /. Following the
modify the PATH line, the/usr/local/apache/bin added, such as: the PATH = $PATH: $HOME/bin:/usr/local/apache/bin.
# source ~/.bash_profile
for this change to take effect. Note: this method only works for the current user. The modification is invalid for other users.
When you find that the new path /usr/local/apache/bin is useless or not needed, you can delete your custom path in the /etc/profile or ~/.bash_profile previously modified.
Step 3:
Add the path to the.profile:
export PATH=”$PATH:/home/lx/anaconda3/bin”
$sudo gedit ~/.profile(or. Bashrc)
$sudo gedit ~/.profile(or. Bashrc)
$sudo gedit ~/.profile(or. Bashrc)
export PATH= “$PATH:your path1:your path2…”
save the file, log out and log in again, the variable takes effect.
variables added this way are only valid for the current user.
$sudo gedit /etc/profile
export PATH= “$PATH:your path1:your path2…”
after the file is edited and saved, restart the system and the variable takes effect.
variables added this way are valid for all users.
$sudo gedit /etc/environment
find the following PATH variable:
PATH=”<
$sudo gedit /etc/environment
PATH=”< . >”
modify the PATH variable by adding your own PATH, for example:
PATH=”< . > : your path1: your path2…”
paths are separated by colons. The file is also rebooted into effect, affecting all users.
note that you are not adding export PATH=… .
method 4: directly under the terminal input
$sudo export PATH=”$PATH:your path1:your path2…
variable takes effect immediately, but the Settings become invalid after the user logs out or the system restarts, suitable for temporary variable Settings. Note: modifications to methods 2 and 3 need to be made with care, especially through root, which can lead to some serious system errors if modified incorrectly. Therefore, I recommend using the first method. Also, embedded Linux development is best not done under root (unless you are already familiar with Linux!!). To avoid serious system errors due to improper operation.
the following is an error for the environment file changes lead to problems and solutions of example:
problem: because not careful in the/etc/environment in environment variables lead to cannot login
tip: don’t set in the/etc/environment export PATH that will lead to can not login system after restart
the solution:
enter command mode in the login interface Alt + CTRL +f1, if not root user need to type (root user is not allowed to be so verbous, gedit edit will not be displayed)
/usr/bin/sudo /usr/bin/vi /etc/environment
cursor move to export PATH** line, press d to delete the line twice;
input :wq save exit;
then type /sbin/reboot to restart the system (it may prompt you to need to boot, at this point direct power off)