RuntimeError: each element in list of batch should be of equal size
1. Example code 2. Running result 3. Error reason 4. Batch_ Size = 25. Analyze reason 6. Complete code
1. Example code
"""
Complete the preparation of the dataset
"""
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, Dataset
import os
import re
def tokenlize(content):
content = re.sub('<.*?>', ' ', content, flags=re.S)
filters = ['!', '"', '#', '$', '%', '&', '\(', '\)', '\*', '\+', ',', '-', '\.', '/', ':', ';', '<', '=', '>', '\?',
'@', '\[', '\\', '\]', '^', '_', '`', '\{', '\|', '\}', '~', '\t', '\n', '\x97', '\x96', '”', '“', ]
content = re.sub('|'.join(filters), ' ', content)
tokens = [i.strip().lower() for i in content.split()]
return tokens
class ImdbDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, train=True):
self.train_data_path = r'E:\Python资料\视频\Py5.0\00.8-12课件资料V5.0\阶段9-人工智能NLP项目\第四天\代码\data\aclImdb_v1\aclImdb\train'
self.test_data_path = r'E:\Python资料\视频\Py5.0\00.8-12课件资料V5.0\阶段9-人工智能NLP项目\第四天\代码\data\aclImdb_v1\aclImdb\test'
data_path = self.train_data_path if train else self.test_data_path
temp_data_path = [os.path.join(data_path, 'pos'), os.path.join(data_path, 'neg')]
self.total_file_path = []
for path in temp_data_path:
file_name_list = os.listdir(path)
file_path_list = [os.path.join(path, i) for i in file_name_list if i.endswith('.txt')]
self.total_file_path.extend(file_path_list)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
file_path = self.total_file_path[idx]
# 获取了label
label_str = file_path.split('\\')[-2]
label = 0 if label_str == 'neg' else 1
# 获取内容
# 分词
tokens = tokenlize(open(file_path).read())
return tokens, label
def __len__(self):
return len(self.total_file_path)
def get_dataloader(train=True):
imdb_dataset = ImdbDataset(train)
print(imdb_dataset[1])
data_loader = DataLoader(imdb_dataset, batch_size=2, shuffle=True)
return data_loader
if __name__ == '__main__':
for idx, (input, target) in enumerate(get_dataloader()):
print('idx', idx)
print('input', input)
print('target', target)
break
2. Operation results
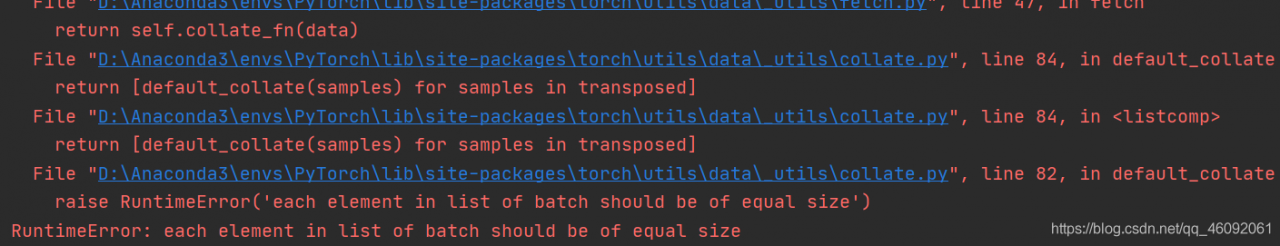
3. Reasons for error reporting
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset=dataset, batch_size=2, shuffle=True)
If batch_ Size = 2 changed to batch_ When size = 1 , no more errors will be reported. The operation results are as follows:

4. batch_ size=2
However, if you want batch_ When size = 2 , how to solve it?
resolvent:
The reason for the problem is the parameter collate in the dataloader_ fn
collate_ The default value of FN is Default customized by torch_ collate, collate_ FN is used to process each batch, and the default default_ Collate processing error.
Solution:
-
first convert the data into a digital sequence and observe whether the results meet the requirements. No similar errors have occurred before using dataloader. Consider customizing a collate_ FN, observations. </ OL>
Here, use method 2 to customize a collate_ FN , and then observe the results:
def collate_fn(batch):
"""
Processing of batch data
:param batch: [the result of a getitem, the result of getitem, the result of getitem]
:return: tuple
"""
reviews,labels = zip(*batch)
reviews = torch.LongTensor([config.ws.transform(i,max_len=config.max_len) for i in reviews])
labels = torch.LongTensor(labels)
return reviews, labels
collate_fn第二种定义方式:
import config
def collate_fn(batch):
"""
Processing of batch data
:param batch: [the result of a getitem, the result of getitem, the result of getitem]
:return: tuple
"""
reviews,labels = zip(*batch)
reviews = torch.LongTensor([config.ws.transform(i,max_len=config.max_len) for i in reviews])
labels = torch.LongTensor(labels)
return reviews,labels
5. Analyze the causes
According to the error information, you can find the source of the error in the collate. Py source code, and the error appears in default_ Collate() function. Baidu found the defaul of this source code_ The collate function is the default batch processing method of the dataloader class. If collate is not used when defining the dataloader_ FN parameter specifies the function, and the method in the following source code will be called by default. If you have the above error, it should be the error in the penultimate line of this function
Source code:
def default_collate(batch):
r"""Puts each data field into a tensor with outer dimension batch size"""
elem = batch[0]
elem_type = type(elem)
if isinstance(elem, torch.Tensor):
out = None
if torch.utils.data.get_worker_info() is not None:
# If we're in a background process, concatenate directly into a
# shared memory tensor to avoid an extra copy
numel = sum([x.numel() for x in batch])
storage = elem.storage()._new_shared(numel)
out = elem.new(storage)
return torch.stack(batch, 0, out=out)
elif elem_type.__module__ == 'numpy' and elem_type.__name__ != 'str_' \
and elem_type.__name__ != 'string_':
if elem_type.__name__ == 'ndarray' or elem_type.__name__ == 'memmap':
# array of string classes and object
if np_str_obj_array_pattern.search(elem.dtype.str) is not None:
raise TypeError(default_collate_err_msg_format.format(elem.dtype))
return default_collate([torch.as_tensor(b) for b in batch])
elif elem.shape == (): # scalars
return torch.as_tensor(batch)
elif isinstance(elem, float):
return torch.tensor(batch, dtype=torch.float64)
elif isinstance(elem, int_classes):
return torch.tensor(batch)
elif isinstance(elem, string_classes):
return batch
elif isinstance(elem, container_abcs.Mapping):
return {key: default_collate([d[key] for d in batch]) for key in elem}
elif isinstance(elem, tuple) and hasattr(elem, '_fields'): # namedtuple
return elem_type(*(default_collate(samples) for samples in zip(*batch)))
elif isinstance(elem, container_abcs.Sequence):
# check to make sure that the elements in batch have consistent size
it = iter(batch)
elem_size = len(next(it))
if not all(len(elem) == elem_size for elem in it):
raise RuntimeError('each element in list of batch should be of equal size')
transposed = zip(*batch)
return [default_collate(samples) for samples in transposed]
raise TypeError(default_collate_err_msg_format.format(elem_type))
The function of this function is to pass in a batch data tuple. Each data in the tuple is in the dataset class you define__ getitem__() method. The tuple length is your batch_ Size sets the size of the. However, one field of the iteratable object finally returned in the dataloader class is batch_ The corresponding fields of the size sample are spliced together.
Therefore, when this method is called by default, the penultimate line of the statement return [default] will be entered for the first time_ Collate (samples) for samples in translated] generate iteratable objects from batch tuples through zip function. Then, the same field is extracted through iteration and recursively re passed in default_ In the collate() function, take out the first field and judge that the data type is among the types listed above, then the dateset content can be returned correctly.
If batch data is processed in the above order, the above error will not occur. If the data of the element is not in the listed data type after the second recursion, it will still enter the next recursion, that is, the third recursion. At this time, even if the data can be returned normally, it does not meet our requirements, and the error usually appears after the third recursion. Therefore, to solve this error, you need to carefully check the data type of the returned field of the dataset class you define. It can also be found in defaule_ The collate() method outputs the batch content before and after processing. View the specific processing flow of the function to help you find the error of the returned field data type.
Friendly tip: do not change the defaule in the source file_ The collate() method can copy this code and define its own collate_ Fn() function and specify its own defined collate when instantiating the dataloader class_ FN function.
6. Complete code
"""
Complete the preparation of the dataset
"""
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, Dataset
import os
import re
import torch
def tokenlize(content):
content = re.sub('<.*?>', ' ', content, flags=re.S)
# filters = ['!', '"', '#', '$', '%', '&', '\(', '\)', '\*', '\+', ',', '-', '\.', '/', ':', ';', '<', '=', '>', '\?',
# '@', '\[', '\\', '\]', '^', '_', '`', '\{', '\|', '\}', '~', '\t', '\n', '\x97', '\x96', '”', '“', ]
filters = ['\.', '\t', '\n', '\x97', '\x96', '#', '$', '%', '&']
content = re.sub('|'.join(filters), ' ', content)
tokens = [i.strip().lower() for i in content.split()]
return tokens
class ImdbDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, train=True):
self.train_data_path = r'.\aclImdb\train'
self.test_data_path = r'.\aclImdb\test'
data_path = self.train_data_path if train else self.test_data_path
temp_data_path = [os.path.join(data_path, 'pos'), os.path.join(data_path, 'neg')]
self.total_file_path = []
for path in temp_data_path:
file_name_list = os.listdir(path)
file_path_list = [os.path.join(path, i) for i in file_name_list if i.endswith('.txt')]
self.total_file_path.extend(file_path_list)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
file_path = self.total_file_path[idx]
label_str = file_path.split('\\')[-2]
label = 0 if label_str == 'neg' else 1
tokens = tokenlize(open(file_path).read().strip())
return label, tokens
def __len__(self):
return len(self.total_file_path)
def collate_fn(batch):
batch = list(zip(*batch))
labels = torch.tensor(batch[0], dtype=torch.int32)
texts = batch[1]
del batch
return labels, texts
def get_dataloader(train=True):
imdb_dataset = ImdbDataset(train)
data_loader = DataLoader(imdb_dataset, batch_size=2, shuffle=True, collate_fn=collate_fn)
return data_loader
if __name__ == '__main__':
for idx, (input, target) in enumerate(get_dataloader()):
print('idx', idx)
print('input', input)
print('target', target)
break
I wish you solve the bug and run through the model as soon as possible!