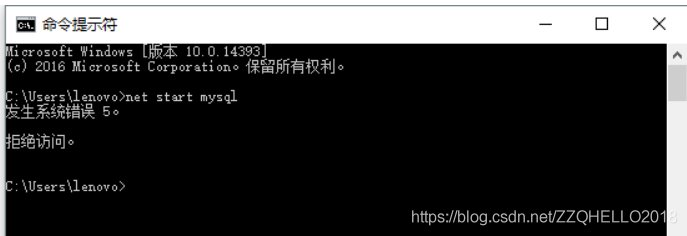
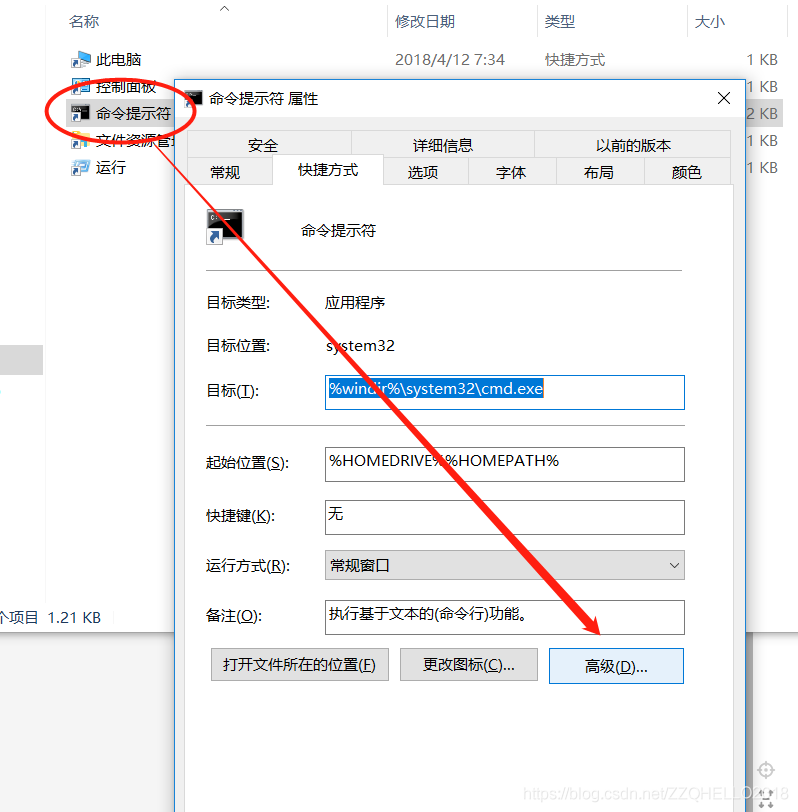
This error is because the CMD permissions are too low and you need to increase the CMD permissions (even if you have administrator privileges).
br> 
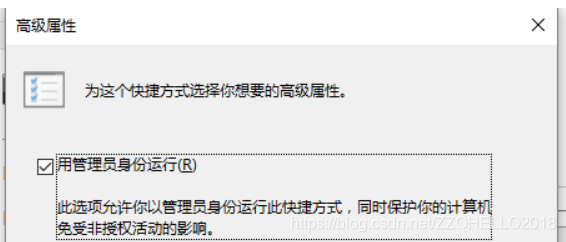
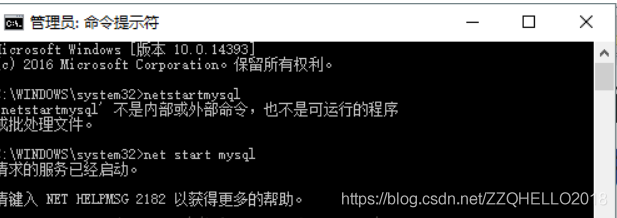
Solution to the incomplete display of big data files printed by pychar
PyCharm opens the file in Python and finds that the prompt file is too large. The file is not fully displayed on the console.
Try the following methods!!
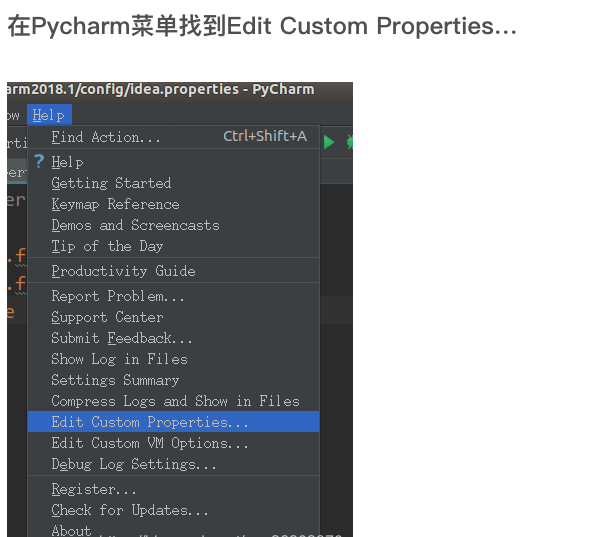
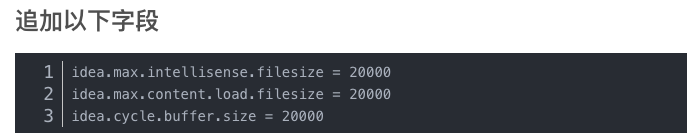
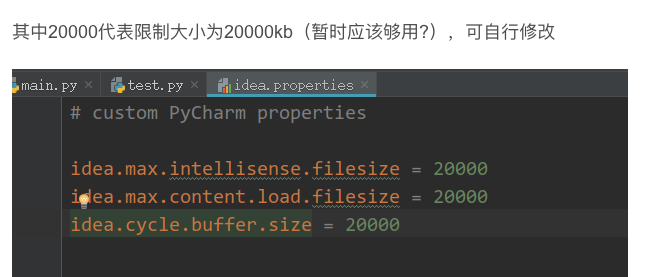
Perfect solution!! If you can’t solve the problem, it is recommended to double check the steps above to see if they are correct
Solution of MySQL data garbled problem
MySQL data garbled to solve the problem
Note for INSERT
The size of the data should be within the specified range of the column. For example, a string with master 80 cannot be inserted into a column with master 40. The data position listed in VALUES must correspond to the permutation position of the column to be added. You can use value in MySQL, but it is not recommended. It has the same function as values. Character and date data should be enclosed in single quotes. Double quotation marks can also be used as delimiters in MySQL. No column is specified or NULL is used to insert a null value.
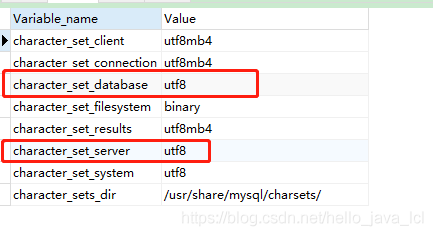
View the encoding of MySQL’s internal Settings
show variables like 'character%';
The solution
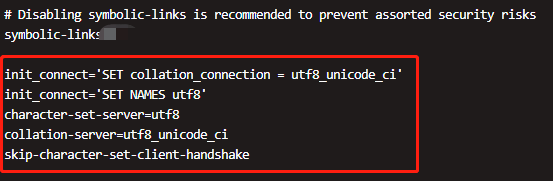
Change the code of Client, Connection and Results to GBK to ensure that it is consistent with DOS command line code
| set | description |
|---|---|
| set GBK character_set_client =; Set character_set_connection= GBK | modify the results of the query character set GBK Set all three at once Note: Exit DOS command line is invalid, need to configure each time Spoop export hive to MySQL
SQOOP Export: mysql> create a Hive table (????)
Like this: 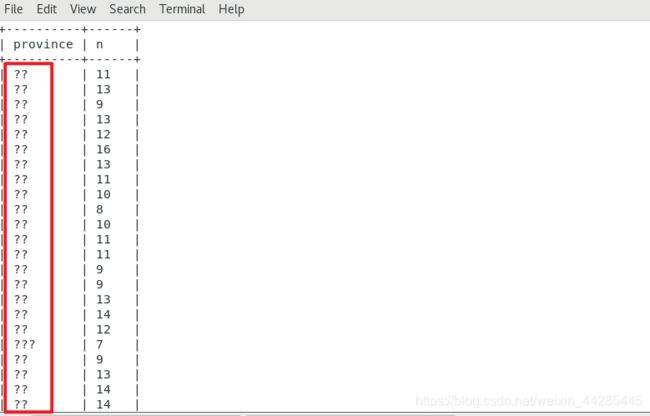 I have modified it once before, and the method works together. However, when the server is changed and the MySQL library is newly created, method one fails to work, and method two takes effect. Method one: Create a new query window, or use the command to enter mysql> , the input Show variables like ‘character%’; View the results:
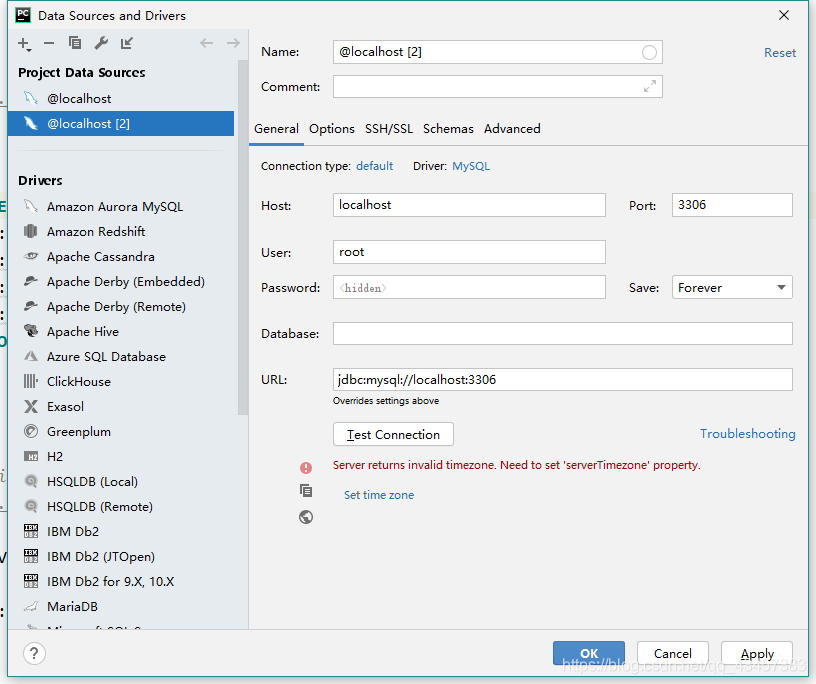
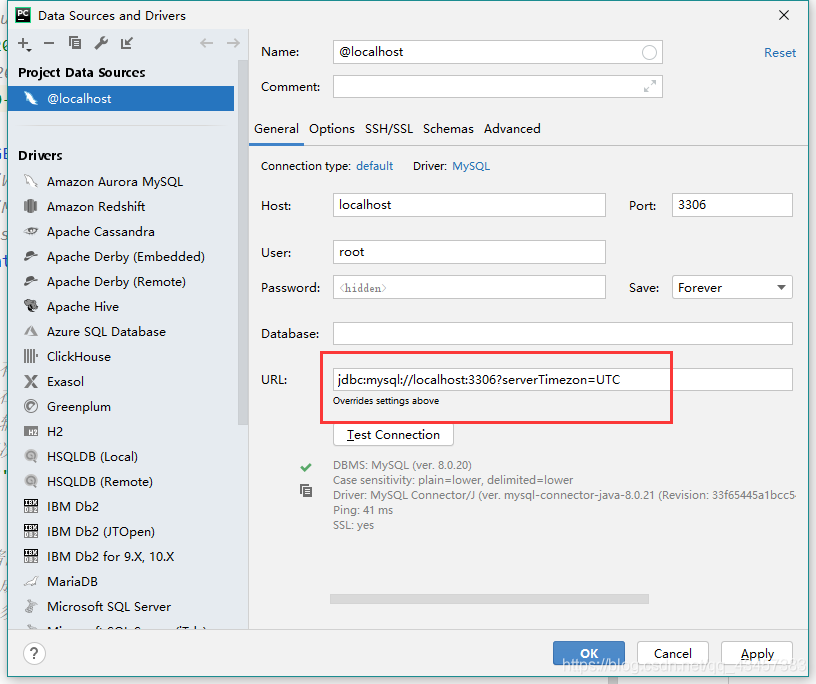
Top35: pychar reports an error when connecting to MySQL server returns invalid timezone. Need to set ‘servertimezone’ propertyTop35: Server returns invalid timezone. Need to set ‘ServerTimezone’ property. Content of the error The problem of master-slave database synchronization stop caused by MySQL deleting data
Mysql master database deletes data from the database if not synchronized to delete the data before the synchronization action stops below for the solution
The first step is to stop slave synchronization service. Step 2: Skip the current error set global sql_slave_skip_counter=10; (Increase the value if the data is deleted) Step 3: Start Slave; Group by query only_ FULL_ GROUP_ By errorThe ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY error in the Group by query The initial version of mysql for Windows (5.7.28) was used in the project, but later when migrating to Linux, some SQL queries experienced the error ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY, because MySQL5.7 default set mysql SQL_mode = ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY attribute, which caused an error (Windows version has no default). PHP – PHP Error[2]: Error while sending QUERY packet. PID=*
In the company project today, such an error occurred when yiIC was used to run the database write operation, as shown in the figure below:
 Project Scenario: A big insert SQL and format for the insert INTO the TABLE VALUES (‘ A ‘, ‘B’, ‘C’), (‘ A ‘, ‘B’, ‘C’), (‘ A ‘, ‘B’, ‘C’)… Code snippet:  It turns out that MySQL’s max_allowed_packet is too small. 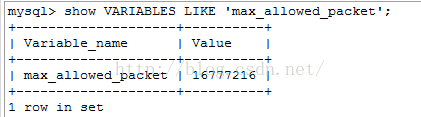 The default max_allowed_packet is only 16M, which will occur if the SQL exceeds the set size. Solutions: 1) Modify the MySQL configuration file Edit my.cnf (My.ini under Windows) in the [mySQld] section or the server configuration section of mysql Max_allowed_packet = 50M (or max_allowed_packet = 50*1024*1024) 2) Command line modification set global max_allowed_packet = 50*1024*1024 Solution to 1030 got error 28 from storage engine in MySQL
Problem Performance:
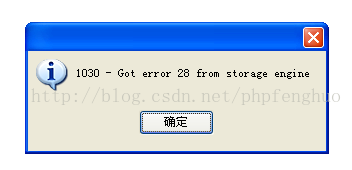 Solutions: Mysql 1030 error does not have enough space, so clean up the disk space and restore normal use. Mysql database had “Got error 28 from Storage Engine” error, so the problem was solved in this way. XML/HTML code
2, XML/HTML code
the reason for this problem: there is not enough temporary space to execute this SQL statement solution: simply point tmpdir to a directory with a large hard disk space Of course, both statements are the same. So there’s almost certainly no space left. I looked at the other disks and sure enough.
An error 1064 is reported when pymysql accesses the image
An error has been reported while accessing images in the mysql database using Pymysql. The code is as follows
Error message: (1064, “You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near ‘\xff\xd8\xff\xe0\x00\x10JFIF\x00\x01\x01\x00\x00\x01\x00\x01\x00\x00\xff\xdb\x00′ at line 1”) I found a lot of methods on the Internet, but I couldn’t solve the problem. Later, I tried again and again and finally solved it Note that the size of the binary BLOB in mysql is smaller than the size of the binary BLOB when designing a table, change the binary data to mediumBLOB The code is as follows: import pymysql from datetime import datetime To create the database, first connect to the mysql database Conn = Pymysql.connect (host=’127.0.0.1′, user=’root’, Database =’ smart_apartment_DB ‘, password=’160507pcsd’, charset=’utf8′) Create a cursor cursor = conn.cursor() The # ExCute () function can execute simple SQL statements f = open(file=’./img/imageOne.jpg’, mode=’rb’) dataimg = f.read() f.close() nowtime = datetime.now().strftime(“%Y-%m-%d, %H:%M:%S”) argdata = pymysql.Binary(dataimg) sqlone = “insert into img_pack(imgtime,imgdata) values(‘%s’,’%s’)” % ( nowtime, argdata) try: cursor.execute(sqlone) conn.commit() except Exception as e: conn.rollback() Print (” Error message: “, e) Close the cursor first cursor.close() Close the database connection again conn.close() After many attempts, the problem was found sqlone = “insert into img_pack(imgtime,imgdata) values(‘%s’,’%s’)” % ( Remove the ‘%s’ single quotation mark from nowtime, argdata and change to sqlone = “insert into img_pack(imgtime,imgdata) values(%s,%s)” Cursor. Execute (SQlone) changed to CURSOR. Execute (SQlone, (nowtime, argdata)) You can store images in a binary stream like mysql The correct code is as follows import pymysql from datetime import datetime To create the database, first connect to the mysql database Conn = Pymysql.connect (host=’127.0.0.1′, user=’root’, Database =’ smart_apartment_DB ‘, password=’160507pcsd’, charset=’utf8′) Create a cursor cursor = conn.cursor() The # ExCute () function can execute simple SQL statements f = open(file=’./img/imageOne.jpg’, mode=’rb’) dataimg = f.read() f.close() nowtime = datetime.now().strftime(“%Y-%m-%d, %H:%M:%S”) argdata = pymysql.Binary(dataimg) sqlone = “insert into img_pack(imgtime,imgdata) values(%s,%s)” try: cursor.execute(sqlone, ( nowtime, argdata) ) conn.commit() except Exception as e: conn.rollback() Print (” Error message: “, e) Close the cursor first cursor.close() Close the database connection again conn.close() Error 1051 (42s02): unknown table ‘…’
The reason Why I reported this error is that the storage engine used MyISAM before, but changed to InnoDB later
But I can’t delete the table because the storage engine mode used for the table before is still MyISAM, so I can’t delete it. 1 species, Modify the storage engine of the table: The second, 1. Delete the file of the corresponding table. Make sure the table is useless before deleting. 2. Find the location of the corresponding library in the system, such as: /var/lib/mysql/ library name MySQL:ERROR 1067 (42000): Invalid default value for ‘end_time’
1. Wrong screenshot
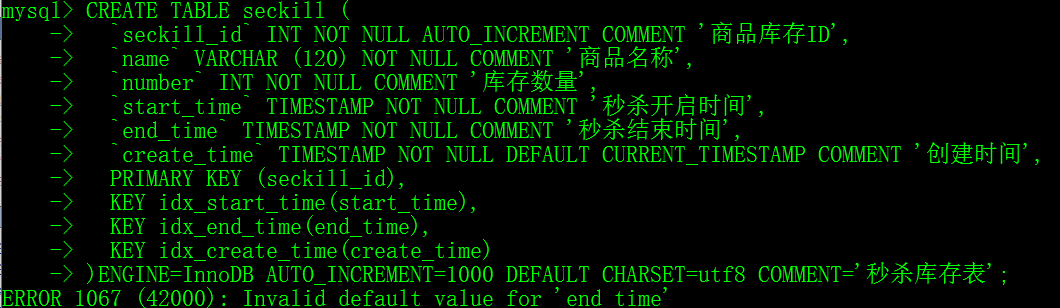 2. Error analysis The first TIMESTAMP column in the table (if not declared NULL or if the DEFAULT or ON UPDATE clause is displayed) automatically assigns the DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP and ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP properties The TIMESTAMP column after the first (if it is not declared NULL or the DEFAULT clause is displayed) automatically allocates DEFAULT ‘0000-00-00 00:00:00’ (zero TIMESTAMP), which does not satisfy the NO_ZERO_DATE in SQL_mode and gives an error. Note: THERE are two types of SQL_mode, one is null value, the other is strict mode, and many default Settings will be given. Strict mode is used by default after MySQL5.7. NO_ZERO_DATE: If this value is set, the MySQL database does not allow insertion of a zero date, which throws an error rather than a warning. 3. Solutions First, execute select @@sql_mode, copy the value of the query and delete the NO_ZERO_DATE, then execute set SQL_mode = ‘modified value’. This method takes effect only in the current session Select @@glob.sql_mode, copy the value of the query and delete the NO_ZERO_DATE, then execute set global SQL_mode = ‘modified value’. This method takes effect in the current service and expires after the MySQL service is re-run Sql_mode = ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION, Then restart mysql. This method is permanent |