|
| SecurityError - contains the environment belongs to the calling code has no right to access security sandbox. To solve this problem, follow these steps:
in the HTML page containing the SWF file, set the following parameters in the object tag of the file: < param name="" value="always" /> in the SWF file, add the following ActionScript: flash. System. Security. AllowDomain (sourceDomain)
Looking at the help instructions above, I think it may be due to cross-domain access issues, as mentioned in the article author (Developer) Control that if SWF wants to communicate with HTML scripts, then the value of allowScriptAccess for the plug-in must be set to Always. And SWF to allow access to the domain. So I try to join in the SWF flash system. Security. AllowDomain (" * "); Then add < < < param name="allowScriptAccess" value="always" /> This sentence.
but the problem is still unresolved. There's no other way to think about it. Later, I found that my DVF could be browsed in the output folder of Project (I built it with Flex), but once I moved to another directory, it was not ok. As a result, I looked up the data and saw the following article, which was called "Overview of Permission Control". This article mainly shows what the Flash Player security model looks like. Below I put up part of the content, interested friends can go to the Internet search.
overview of permission control
Flash Player client runtime security model is a model designed around object resources such as SWF files, local data, and Internet urls. "Resource holders" means the parties that own or use these resources. Resource holders have control over their own resources (security Settings), and each resource has four holders. Flash Player USES a strict hierarchy of rights for these controls, as shown in the figure below:
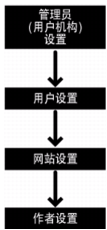
security control hierarchy
the figure shows that if an administrator restricts access to a resource, no other holder can override the restriction.
administrative user control
The administrative user of the computer (the user logging in with administrative privileges) can apply Flash Player security Settings that affect all users of the computer. In a non-enterprise environment, such as a home computer, there is usually only one user, who also has administrative access. Even in an enterprise environment, a single user can have computer administration rights.
There are two types of administrative user control:
MMS. CFG file "global Flash Player trust" directory
MMS. CFG file
on Mac OS X, the MMS. CFG file is located in /Library/Application Support/Macromedia. On Microsoft Windows system, the file is located in the system directory of the Macromedia Flash Player folder (for example, in the default install Windows XP to C:/Windows/system32/macromed/Flash/MMS CFG).
Flash Player will read its security Settings from this file when it starts, and then use these Settings to restrict the functionality.
The MMS. CFG file includes Settings that the administrator USES to perform the following tasks:
data loading - restricts reading of local SWF files, prohibits file downloading and uploading, and sets storage limits on permanent Shared objects. privacy controls - disable microphone and camera access, prohibit SWF files from playing windowless content, and prohibit SWF files from accessing permanently Shared objects in domains that do not match the URL displayed in the browser window. Flash Player updates - sets the time interval to check Flash Player updates, specifies the URL to use to check Flash Player updates, specifies the URL from which to download Flash Player updates, and completely disables automatic Flash Player updates. older file support - specifies whether earlier versions of SWF files should be placed in a trusted local sandbox. local file security - specifies whether a local file can be placed in a trusted local sandbox. full screen mode - disable full screen mode.
SWF file can be by calling the "Capabilities. AvHardwareDisable and " Capabilities. LocalFileReadDisable property to access functionality disabled some of the information. However, most of the Settings in the MMS.cfg file cannot be queried through ActionScript.
is to enforce application-independent security and privacy policies on the computer, and only the mms.cfg file can be modified by the system administrator. The MMS. CFG file cannot be used to install the application. While an installer running with administrative permissions can modify the contents of the MS.cfg file, Adobe considers such use a violation of the user's trust and advises the creator of the installer never to modify the MS.cfg file.
global Flash Player trust directory
The administrative user and installation application can register the specified local SWF file as trusted. These SWF files are assigned to trusted local sandboxes. They can interact with any other SWF file or load data from anywhere (remote or local). The file is specified as trusted in the global Flash Player trust directory, the same directory as the mms.cfg file, in the location (specific to the current user) as follows:
The Windows: the system/Macromed/Flash/FlashPlayerTrust (for example, C:/Windows/system32/Macromed/Flash/FlashPlayerTrust) Mac: App support/Macromedia FlashPlayerTrust (for example,/Library/Application support/Macromedia/FlashPlayerTrust)
The Flash Player trust directory can contain any number of text files, with each file listing the trusted path on one line. Each path can be a single SWF file, HTML file, or directory. Comment lines start with #. For example, a Flash Player trust profile with the following text indicates that trusted status is granted to all files in the specified directory and all subdirectories:
# Trust files in the following directories:
C:/Documents and Settings/All Users/Documents/SampleApp
The path listed in the trust profile should always be the local path or the SMB network path. Any HTTP path in the trust profile will be ignored; Only local files can be trusted.
to avoid conflicts, specify a filename for each trust profile that corresponds to the installed application, and use the.cfg file extension.
because developers distribute locally running SWF files by installing the application, you can have the installation application add a configuration file to the global Flash Player trust directory, granting full access to the files to be distributed. The installation application must be run by a user with administrative rights. Unlike the MMS.cfg file, the global Flash Player Trust directory is included to enable the installation application to grant trust permissions. Both managing users and installing applications can specify trusted local applications using the Global Flash Player Trust directory.
after reading this article, it turns out that the project in Flex actually adds the output file from the project to the local trust sandbox. The CFG documentation for Flex was also found in the local directory specified, which does include the output folders for each project. So I also tried to add the directory where the DVF was in to the local trust sandbox. The entire folder path string is written to a text file based on the CFG file format described in the article, and then saved as a CFG file. Put it in the system/Macromed/Flash/FlashPlayerTrust. Then run the DVF again, the error message is gone, and the problem is resolved.
in retrospect, Flash Player is really getting stricter with security. The current version is so strict even for local runs (the version I used before was 9.0, so long as You set allowScriptAccess to always in HTML). Only a thorough understanding of Flash Player's security mechanisms can help us solve the problem better. However, I use above is the management of user control method to achieve, so it is the highest level of configuration, there may be relatively large security risks, you can also try to use the ordinary user control method to add trust. The article write here, hope to be helpful to everybody.
Recently, I participated in a virtual community Project, in which I made a farm game and video conferencing application module. The whole Project has several Flex projects, including the main program, public library and various functional modules. Because I was a late participant, I did not know much about the development mode of the Project, and of course because the two applications I made were independent, So I used the independent Flex Project to build the two applications.
The project used RSL(Runtime Shared Library) to link external libraries, so I also used RSL when making those two applications. At the beginning, everything was normal. After the project was launched, the customer service staff occasionally received a call from the customer saying that the farm could not be opened, and the location of the farm appeared “RSL Error 1 of 1”, with a paragraph below “Error #2032: flow Error”. URL: http://www.xxx.com/XXX.swf/ [[DYNAMIC]]/framework_3 2.0.3958. SWF.
For a period of time, I was quite confused. At that time, I found the cause of the problem and came up with a solution.
First make a brief introduction of RSL, RSL is to compile multiple Project to create classes to multiple SWF, which includes the class library Project, the Flex framework library (framework_xxx. SWF), so that you can put the SWF contained in class sharing for multiple projects, on the client side load when it is ok to only need to load a (if not using RSL, all use class will compile into a SWF, if there are multiple SWF, repeat each part is contained inside the class, increase the user downloads). In the case of only one Project, the effect of using the RSL is not obvious because the generated SWF needs to be loaded for all other SWF Shared libraries that are used; However, if there are multiple projects, the advantage will emerge. After the first SWF loads the Shared library, the later SWF will not need to be loaded again, which can improve the access speed.
After using RSL, there will be two framework files “framework_3.2.0.3958. SWZ” and “framework_3.2.0.3958. SWF” in the root directory of the generated project (using different Flex SDK, the latter version number of these two framework files will be different). If the framework.swz file fails to load, Flash Player will go to the framework.swf file, one of the two is successfully loaded, and the project will run correctly.
In the event of a “RSL Error” Error, I tried to reproduce this Error on your computer, operating system, using XP when I cancel the SWZ files from the Flash Player cache, and built an empty read-only SWZ files, name and just delete the SWZ file name, to run the project again, and sure enough the “RSL Error”, below, write a new framework for Flash Player to the cache. SWZ failed, at the same time framework. The SWF also failed to load. The solution was to manually save the framework.swz file to the client’s Flash Player cache. I didn’t think much about why the file didn’t load successfully on the client’s computer (maybe it was a permission issue), but I just posted on the forum to see if anyone had a similar problem.

Everyone has a lazy side, which was exactly what I did at that time. If you think about it carefully, there are at least two questions that should be explored: 1. The whole project is using RSL, why only the two applications I wrote have RSL errors, and what is the difference between the application I wrote and the whole project; 2. 2, my application in framework. SWZ failed to load, framework. SWF also failed to load, so it can not run, the whole project in SWZ failed to load, but can run, later look, IE cache does exist framework. SWF, then this can be the whole project file load framework. SWF.
For a while, no one on the forum was sure of a solution to the problem. Once again, let me dig into this problem to help a customer solve the farm can not be opened, that is, there is an “RSL Error”. The client’s computer is Vista and Internet Explorer 8. When I put the framework.swz used in RSL into the client’s Flash cache, it occurred to me that it might be caused by the operating system. We are developing on XP. Because there is no SWZ file in the client’s Flash cache, the previous access failed to load the SWZ at all.
I installed Win7 in the virtual machine to do the test (Win7 and Vista kernel), sure enough, under Win7 can not normally access the farm, Flash cache without SWZ file. Because the project of other modules can be normal visit, so I think framework. The SWF file should be loaded successfully, but when I open the IE cache, find IE cache is framework. SWZ, rather surprised, as the chart, because always thought before the SWZ framework cache files will be saved to Flash, never think under Windows 7 will be put into IE cache (I Flash Player version is 10.0.45), which is why no SWZ framework in the Flash cache files. (If frame. SWZ is in Flash cache, SWFS in multiple domains can be Shared; if in IE cache, SWFS in the same domain can only be Shared).
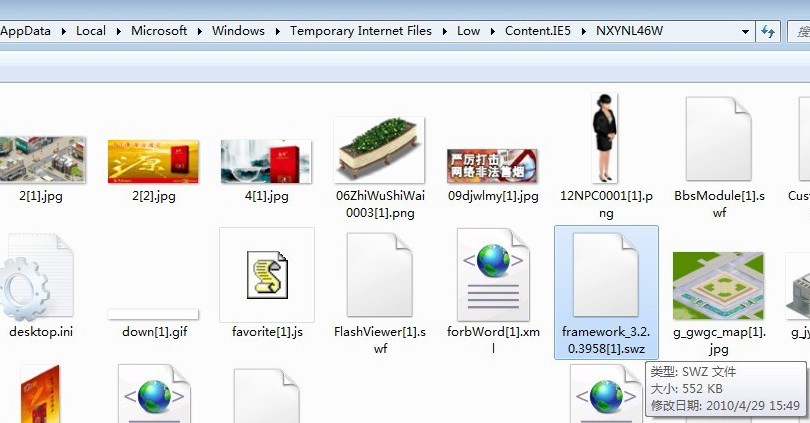
Discovering this has certainly given me a better understanding of the RSL bug, which could be a bug in Flash Player, or a manipulation of Adobe by Microsoft, but this cannot be confirmed at this time.
Question to this, of course, is not the end, because we have a question: framework. SWZ loading failure, and framework. The SWF can choose ah, why the second choice is also failed, I use firefox HttpFox plugin to view the request to the server client, finally found the problem, and it is concluded that the second question framework. SWF loading failure has nothing to do with the operating system. Summary of the cause of the problem: “Loading an external SWF file that USES an RSL causes an error path to the Framework file that the external SWF points to.”
Firefox browsing, and open the HttpFox plugin to view the Http request, after loading the main routine, can detect the client request the framework. SWZ file (if the SWZ cannot load may be loaded framework. The SWF file), when I disable the SWZ file after loading, into the farm, found the farm reload framework. SWZ and framework. The SWF, but these two files are failed to load, the two pictures below the first one is the main process successfully loaded framework. SWZ, The second path to the Framework file that shows the farm loaded is an error.
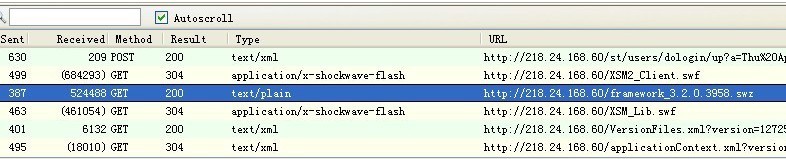
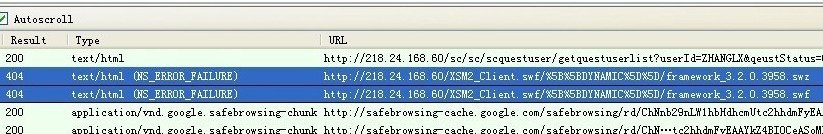
The problem is clear, the farm is a separate Project and USES the RSL and is loaded into the main program using Loader. It looks as if this changes the URL path of the farm program, but the resource path used by the farm does not change. So the conclusion should be that only the path of framework file used by this application is changed, and this path is only used in Flash Player, I don’t know if there is any other place to set it, is this another Flash Player bug?
I hope to further study the RSL.
PS: I forgot to write the solution in this article. At present, I know of two solutions. One is to stop using the RSL. The second is to manually copy the FlashPlayer cache file to the client. The disadvantage of this method is that sometimes we cannot operate the client. For the second approach, the cache directory of FlashPlayer is: XP system is C:/Documents and Settings/user/Application Data/Adobe Flash Player/AssetCache/H7UC3H3Y, VISTA and Windows 7 system is C:/Users/username/AppData/Roaming/Adobe Flash Player/AssetCache/RAU4Y963, this the end of the two paths a folder name is random, Another copy SWZ file also need to pay attention to in the past, such as FlexSDK3.2 SWZ filename in the cache is 1 c04c61346a1fa3139a37d860ed92632aa13decf. SWZ, this files need to be from a flashplayer cache is a problem with the copy machine to machine.
Recently discovered a flex modules loaded trigger dragManager error, in the main application inside put a moduleLoader to load module, put the two buttons to control the repeated load, according to the first load module, a button press another button to uninstall the module, using the moduleLoader load method, loading unloading using unloadModule () method, module placed in a datagrid, found in the testing process, when to reload the module, Is also carried out a unloadModule method and then press the first button to reload the module, if this time to click on any one line will appear inside the datagrid: TypeError: Error # 1034: the Type Coercion failed: always convert. mx managers: : DragManagerImpl@12631a61 converts to the error mx.managers.idragmanager . After a long search on Google, I finally found the solution on a foreign forum. It is as simple as adding import mx.managers.DragManager into the main application. private var dragManager: dragManager; these two sentences will solve the problem. As for why can appear such circumstance, find an explanation for the others on the Internet, the following is from Google a flex discussion group of other people’s answer (HTTP:// groups.google.com/group/riadev/tree/browse_frm/month/2007-05/5eeebf64e4926c45?rnum=11& _done = % 2 fgroup % 2 friadev % 2 fbrowse_frm % 2 fmonth % 2 f2007-05% 3 f)
QUOTE:
This is Shared code for Module,
this problem tends to occur when managers are used in a Module (such as PopUpManager, DragManager, HistoryManager),
manager’s methods are static methods, and a singleton of this manager interface is created throughout the application,
but a module USES this singleton only in its own Application domain, when multiple modules use the same singleton and main
This empty object reference problem occurs when the
application is not in use: a module that first introduces a manager cannot follow the singleton of the manager interface
is Shared by other modules. When other modules call the method of the Manager, the application will not create the instance of the Manager interface any more, so this module cannot refer to the instance of the Manager interface, which causes the problem of empty object reference. You can refer to Flex source code.
Accordion and TabNavigator’s historyManagementEnabled = by default
true; And ViewStack’s historyManagementEnabled = false;
so be aware of HistoryManager’s Shared code issues when using TabNavigator and Accordion. This problem also occurs when only one module USES HistoryManager and that module is loaded after uninstalling, indicating that the second load is equivalent to a new module.
a solution:
introduces the relevant manager in the main application by declaring the reference of the manager in the main application, as follows:
import mx.managers.HistoryManager;
var historyManager:HistoryManager;
other managers are similar.
can also load the Shared code into the main application domain as a module, which can be explained in detail by referring to Alex
Harui PPT:
Speak http://blogs.adobe.com/aharui/presentations/ below the presentation about the module, very detailed.
FLEX publishing size is known to every FLEX developer as
because when FLEX is published it comes with a frame file that contains all the FLEX built-in classes…
the file size is about 500 K, so it’s an empty FLEX project. There are over 500 K
so FLEX provides the RSL(runtime Shared library).
lets the user download the same version of the frame file only once and store it in the cache directory specified by FlashPlayer.
the next time you browse the FLEX project that applies the RSL, you do not need to download again.. Thus speeding up the loading speed.
… Theories don’t express much… Something like this… Let’s actually do it…
to apply RSL, we perform the following steps :
1. Right-click in the project folder, and select “properties”-“Flex BuildPath”-“Library Path”
2. On the TAB, we see “FrameWork Linkage “. By default, “Merged into Cdoe “is selected. 3. Click “runtime Shared library(RSL)”, click “OK”
so that our project is already using the RSL~ to separate the frame files…
let’s open the bin(bin-debug) folder of our project.
will see that we have generated framework_3.0.0.477. SWF and framework_3.0.0.477. SWZ two files (0,0,447 is the version number). Has become around 50k (only two or three components)
when we publish the project..
just need to framework_3.0.0.477. SWF and framework_3.0.0.477. SWZ
and project SWF in the same directory to the server…
ps: here to talk about two noteworthy problems..
the first one is RSL error after the release of the project.. There are two main reasons :
1. Using FLASH PLAYER less than version 9.0.115,
2. Framework_3.0.0.477. SWF and framework_3.0.0.477. SWZ did not upload to the server.. So that the library cannot be downloaded…
say the second question before.. First introduce the framework_3.0.0.477. SWF and framework_3.0.0.477. SWZ,
where framework_3.0.0.477. When the load is successful.. It will be placed in the Flash Player cache directory.
while framework_3.0.0.477. SWZ download failed.. Flashplayer will automatically download framework_3.0.0.477.swf. The file can only be downloaded to ie cache..
very much from friends reflection.. While browsing locally.. Framework_3.0.0.477. SWZ can be loaded into the player’s cache directory.
but when placed on the server.. That will load unsuccessful.. Can only run by loading SWF..
occurs in this case.. Because server IIS does not support SWZ suffix file download..
(this has happened before before FLV was not prevalent),
if it is your own server. All we need to do is configure IIS. Add a MIME type…
detail operation will not say.. The MIME type is as follows..

refer to: http://helpx.adobe.com/flash-player/kb/flash-builder-flash-player-throws.html
Error message: SecurityError: Error #2148: SWF file C:/Documents and Settings/Administrator/Adobe Flash Builder 4/domain_mgr_flex/bin – debug/domain_mgr_main. SWF cannot access the local resources C:/Documents and Settings/Administrator/Adobe Flash Builder 4/domain_mgr_flex/bin – debug/textLayout_4 0.0.10485. SWF. Only file system-limited SWF files and trusted local SWF files can access local resources. at flash.net: : URLStream/load () at flash.net: : the URLLoader/load ()
the solution:
in the C: \ WINDOWS \ system32 \ Macromed \ Flash \ FlashPlayerTrust directory (if FlashPlayerTrust directory does not exist, can create a) add a file, such as: True.txt (file name can be anything from), C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\Adobe Flash Builder 4\ Flex workspace path, of course, can also be set to C:\
or all the disc characters can be written:
C:\
D:\
E:\
F:\
Note: You will need to restart your browser after editing this trust.txt file.
Originally, I had FlashBuilder4.0 installed on my machine, so I didn’t have this problem when debugging SWF. FlashBuilder4.7 was installed later, but version 4.0 was not uninstalled, so running SWF in the 4.0 compiler will report this error, while version 4.7 will not, presumably due to workspace path conflicts.
Strangely, errors are only reported in Firefox, but not in IE. It seems that the Flashplayer of these two browsers is quite different.
|





