I. Function overview
The main function of DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is to centrally manage and assign IP addresses, so that hosts in the network environment can dynamically obtain IP address, Gateway address, DNS server address and other information, and improve the utilization rate of addresses.
DHCP protocol adopts the client/server model: When the DHCP server receives the address application information from the network host, it will send the relevant address configuration information to the network host to realize the dynamic configuration of the network host address information.
Ii. Working principle
DHCP USES UDP as the transport protocol. The host sends the request message to port 67 of DHCP server, and the DHCP server responds the reply message to port 68 of the host. The detailed interaction is as follows.
(1) DHCP Client sends DHCP Discover message by broadcasting.
- (2) all DHCP servers can receive DHCP Discover message sent by the DHCP Client, and all DHCP servers will give a response and send a DHCP Offer message to the DHCP Client. (3) The “Your(Client) IP Address” field in the DHCP Offer packet is the IP Address that DHCP Server can provide to THE DHCP Client, and DHCP Server will put its IP Address in the “Option” field so that DHCP Client can distinguish different DHCP servers. The DHCP Server will have a record of the assigned IP address after sending this message. (4) DHCP Client can only handle one DHCP Offer packet among them, and the general principle is that DHCP Client can handle the DHCP Offer packet that it receives first. (5) The DHCP Client will send a broadcast DHCP Request message, and add the IP address and the required IP address of the selected DHCP Server into the option field. (6) After the DHCP Server receives the DHCP Request message, it shall determine whether the IP address in the option field is the same as its own address. If it is not the same, DHCP Server does not do anything but clear the corresponding IP address assignment record; If the same is true, the DHCP Server will respond to the DHCP Client with a DHCP ACK packet and add the usage lease information for the IP address in the options field. (7) After the DHCP Client receives the DHCP ACK packet, it shall check whether the IP address assigned by the DHCP Server can be used. If it can be used, then the DHCP Client successfully obtains the IP address and automatically starts the renewal process by using the lease term according to the IP address; If the DHCP Client finds that the assigned IP address has been used, the DHCP Client will send the DHCP Decline message to the DHCPServer, notify the DHCPServer to disable this IP address, and then the DHCP Client will start the new address application process. (8) After the DHCP Client successfully obtains the IP address, it can Release its IP address at any time by sending THE DHCP Release message. After the DHCP Server receives the DHCP Release message, it will recover the corresponding IP address and reassigned it. 3. Experimental verification: After DHCP services are configured on servers and network devices (routers and switches), DHCP can generally be used as DHCP servers. In this experiment, routers were used to simulate the network topology, as shown in the figure below: In the
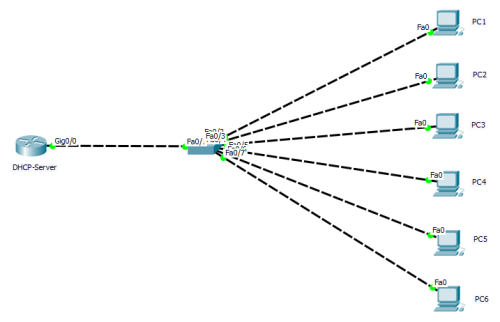 diagram, routers were dhCP-server and switches were two-layer devices (switch ports connected to PC1-6 hosts were all in the default VLAN 1).
diagram, routers were dhCP-server and switches were two-layer devices (switch ports connected to PC1-6 hosts were all in the default VLAN 1). 1. Before the configuration of dhcp-server is completed, PC1 is configured to DHCP to get the IP address, which is shown as follows:
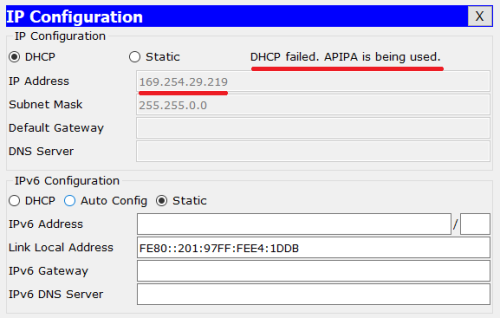
The result shows “DHCP failed. APIPA is being used”, indicating that the IP address was not successfully obtained (generally a “169.254.0.0/16” segment address is displayed, indicating that the IP address was not obtained from the DHCP server).
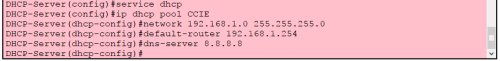
2. Configure DHCP related information on the router:
(1) configure port IP as shown in the figure below:

(2) configure DHCP service as shown in the figure below:
3. At this point, verify the IP address acquisition above PC1:
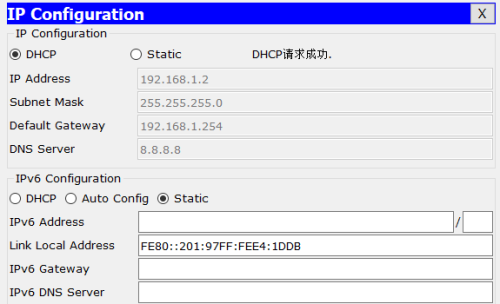
As can be seen from the figure above, PC1 successfully obtained the CONFIGURATION information of IP address, gateway, DNS-Server, etc.
Reproduced in: https://blog.51cto.com/13401027/1977218