Du [- abcdhhklmssx] [- L & lt; symbolic link & gt;] [- X & lt; file & gt;] [– block size] [– exclude = & lt; directory or file & gt;] [– max depth = & lt; directory level & gt;] [– help] [– version] [directory or file]
Common parameters:
-A or – all displays disk usage for each specified file, or for each file in the directory.
-B or – bytes displays the size of the directory or file in bytes.
-C or – total displays not only the size of the directory or file, but also the sum of all the directories or files.
-D or – dereference args displays the source file size of the specified symbolic connection.
-H or – human readable in units of K, m and G to improve the readability of information.
-H or – Si is the same as – H, but K, m and G are converted to 1000 instead of 1024.
-K or – kilobytes in 1024 bytes.
-L or – count links repeatedly calculate the file of hardware connection.
-L & lt; symbolic connection & gt; or – dereference & lt; symbolic connection & gt; displays the source file size of the symbolic connection specified in the options.
-M or – megabytes in 1MB.
-S or – summarize displays only the total, the size of the current directory.
-S or – separate dirs displays the size of each directory, excluding the size of its subdirectories.
-X or – one file Xsystem is based on the file system at the beginning of processing. If there are other different file system directories, they will be omitted.
-X & lt; file & gt; or – exclude from = & lt; file & gt; specify a directory or file in & lt; file & gt.
– exclude = & lt; directory or file & gt; skips the specified directory or file.
– max depth = & lt; the number of directory layers & gt; is ignored when the number of directory layers exceeds the specified number.
– help displays help.
– version displays the version information.
1 & gt; to display the disk usage of a directory tree and each subtree
du /home/linux
This shows the number of disk blocks in the / home / Linux directory and each subdirectory.
2 & gt; to display the disk usage of a directory tree and each subtree in 1024 bytes
du -k /home/linux
This shows the number of 1024 byte disk blocks in the / home / Linux directory and each subdirectory.
3 & gt; displays the disk usage of a directory tree and each subtree in MB
du -m /home/linux
This shows the number of MB disk blocks in the / home / Linux directory and each subdirectory.
4 & gt; displays the disk usage of a directory tree and each subtree in GB
du -g /home/linux
This shows the number of GB disk blocks in the / home / Linux directory and each subdirectory.
5 & gt; view the size of all directories and subdirectories under the current directory:
du -h .
“.” represents the current directory. It can also be changed to a clear path
-H means to display in the humanized form of K, m and G
6 & gt; view the size of the user directory in the current directory, and do not want to see other directories and their subdirectories:
du -sh user
-S means to summarize, that is, only one summarized value is listed
du -h –max-depth=0 user
–Max depth = n means only to drill down to the n-th level directory. If it is set to 0, it means not to drill down to the subdirectory.
7 & gt; list the sizes of all directories and files in the user directory and its subdirectories:
du -ah user
-A means including directory and file
a
8 & gt; lists the size of the directory in the current directory whose name does not include the XYZ string:
du -h –exclude=’*xyz*’
9 & gt; want to list more information about the size of the user directory and subdirectories in one screen:
du -0h user
-0 (zero bar) indicates that the information of each directory listed is directly output to the next directory instead of newline.
10 & gt; displays all disk usage for only one directory tree
du -s /home/linux
11 & gt; view the size of each folder: Du – h — max depth = 1

To view the specified directory:
The code is as follows: where / path represents the path
du -h --max-depth=1 /pathThe details are as follows:
root@ubuntu4146:~# du -h --max-depth=1 /data/
1.1G /data/gitlabDataa
8.0K /data/test
241G /data/gitlabData
809G /data/home
15G /data/OpenGrok
16K /data/lost+found
1.1T /data/
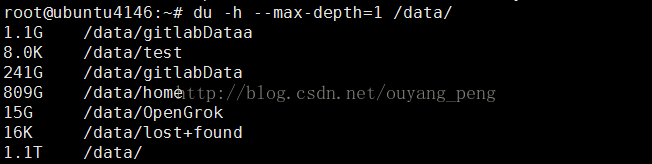
We find that the / data / home / directory takes up the most, so we can continue to see which directory takes up the most, as follows:
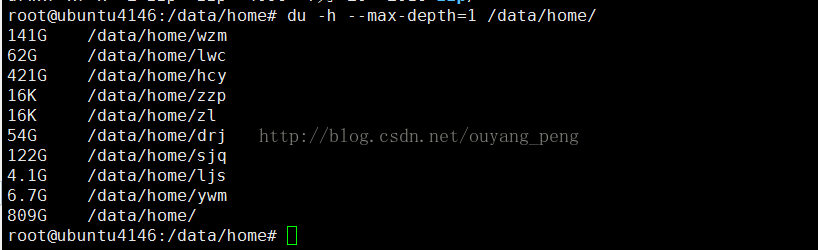
root@ubuntu4146:/data/home# du -h --max-depth=1 /data/home/
141G /data/home/wzm
62G /data/home/lwc
421G /data/home/hcy
16K /data/home/zzp
16K /data/home/zl
54G /data/home/drj
122G /data/home/sjq
4.1G /data/home/ljs
6.7G /data/home/ywm
809G /data/home/
root@ubuntu4146:/data/home#
Author: Ouyang Peng welcome to reprint, share with others is the source of progress!
Please keep the original address: http://blog.csdn.net/ouyang_ peng/article/details/10414499
