comes first
a little in-depth understanding of Mali’s architecture, compare the basic process of the existing GPU with that of Mali, and propose the advantages and disadvantages of the GPU. The original address: https://developer.arm.com/graphics/developer-guides/tile-based-rendering
Traditional GPU
the architecture of a traditional GPU is generally called the Immediate mode GPU. The main process is vertex shader and fragment shader executed sequentially. The pseudocode is:
for draw in renderPass:
for primitive in draw:
for vertex in primitive:
execute_vertex_shader(vertex)
for fragment in primitive:
execute_fragment_shader(fragment)
The
data stream looks like this:
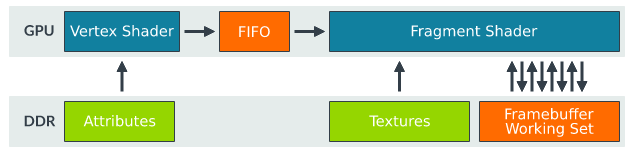
Advantages of
The main advantage of
is that the output from vertex stays on the chip and can be read directly and quickly in the next stage.
shortcomings
if there are large graphics (mostly triangles) that need to be rendered, then the framebuffer will be very large. For example, rendering the color of the entire screen or deep rendering will consume a lot of storage resources, but there are no such resources on the chip, so the DDR will be read frequently. Many operations related to the current frame (such as blending, depth testing or stencil testing) all need to read this working set, so the bandwidth required is huge and the energy consumption is also high. For mobile devices, this way is not conducive to the operation of the device.
Tile-based GPU
so Mali’s GPU proposed the Tile-based concept, which is to divide the image into 16*16 pieces. Rendering in small chunks and writing to DDR solves this problem by reducing the frequency of reading and writing to DDR. But chunking requires knowing the geometry of the entire image, so the operation is broken down into two steps:
- first step to perform geometry related operations, and generate tile list.
- second step to execute fragment operation on each tile, after completion, write memory
The
pseudocode is as follows:
# Pass one
for draw in renderPass:
for primitive in draw:
for vertex in primitive:
execute_vertex_shader(vertex)
append_tile_list(primitive)
# Pass two
for tile in renderPass:
for primitive in tile:
for fragment in primitive:
execute_fragment_shader(fragment)
data flow as follows:
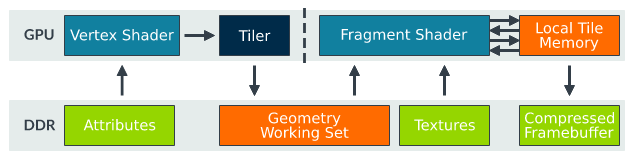
Advantages of
obviously solves the bandwidth problem of the traditional model, because the fragment shader reads a small fragment every time and puts it on the fragment. There is no need to read the memory frequently until the last operation is finished, and then write to the memory. You can even further reduce reads and writes to memory by compressing tiles. In addition, when some areas of the image are fixed, the function is called to determine whether tiles are the same, so as to reduce repeated rendering.
shortcomings
is used to write the output geometry to the DDR after the vertex phase, and then to be read by fragment shader. This is the balance between the overhead of tile writing DDR and the overhead of fragment Shader rendering reading DDR. Another operation, such as Tessellation, is not suitable for the Tile-based GPU.
summary
now the resolution of the screen is getting bigger and bigger from 1080p to 1440p to 4K, you can see, Mali’s architecture will be used on a large scale in the future.
but there are some pitfalls that developers need to avoid. The first is to properly set the Render Pass to take advantage of the features of the architecture; The second is to understand the benefits of this geometric division.