The reason is an error caused by my declaration of variables after the case
Analysis of this problem:
Due to switch a few case statement in the same scope (because a case statement is label, but they belong to a switch beyond constant-like block), so if in some case the following statement variables, the scope of the object is between two curly braces, that is, the entire switch statement, other case statement can also see that such things can lead to errors. We can do this by adding curly braces to the statements that follow the case. The reason for the braces is to specify the scope of the variables we are declaring, just in this case. In fact, to write the switch-case statement more formally, we should add curly braces after the case statement.
Source code is as follows:
Analysis of this problem:
Due to switch a few case statement in the same scope (because a case statement is label, but they belong to a switch beyond constant-like block), so if in some case the following statement variables, the scope of the object is between two curly braces, that is, the entire switch statement, other case statement can also see that such things can lead to errors. We can do this by adding curly braces to the statements that follow the case. The reason for the braces is to specify the scope of the variables we are declaring, just in this case. In fact, to write the switch-case statement more formally, we should add curly braces after the case statement.
Source code is as follows:
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int zt_num1 = 1, zt_num2 = 2;
if (argc < 2) {
printf("please input again\n");
return -1;
}
if (!argv[1]) {
printf("please input again\n");
return -1;
}
switch(*argv[1])
{
case '+':
zt_num1 = zt_num1 + zt_num2;
break;
case '$':
zt_num1 = zt_num1 - zt_num2;
break;
case '#':
int num = 3;
zt_num1 = zt_num1 + zt_num2 + num;
break;
default:
printf("please input again\n");
break;
}
printf("%d\n", zt_num1);
return 0;
}
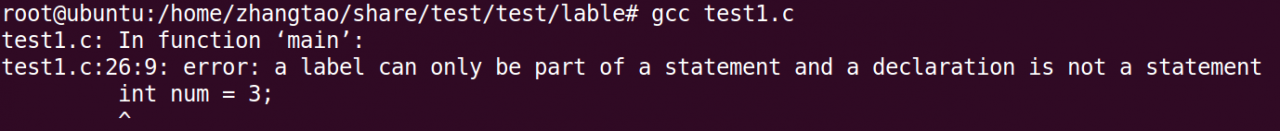
The compilation results are as follows:
The modified code is as follows:
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int zt_num1 = 1, zt_num2 = 2;
if (argc < 2) {
printf("please input again\n");
return -1;
}
if (!argv[1]) {
printf("please input again\n");
return -1;
}
switch(*argv[1])
{
case '+':
zt_num1 = zt_num1 + zt_num2;
break;
case '$':
zt_num1 = zt_num1 - zt_num2;
break;
case '#':
{
int num = 3;
zt_num1 = zt_num1 + zt_num2 + num;
break;
}
default:
printf("please input again\n");
break;
}
printf("%d\n", zt_num1);
return 0;
}
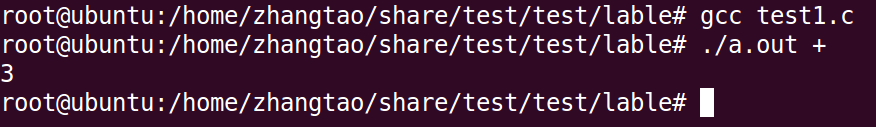
The compilation and operation results are: