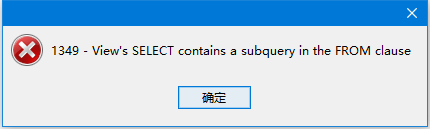
0x02 Detailed description of the bug (a little too much to highlight the bolded parts).
https://bugs.mysql.com/bug.php?id=12755
How to locate this bug
Search for view contains subquery, find the following bug (a circle…)
ErrorCode 1379: View’s SELECT still can’t contain a subquery
—————————————————————————
[3 May 2012 8:42] Arjan Saly
Description: Already reported in 2006 for version 5.0, still not solved in 5.5: When creating a view, subqueries are still not allowed in the SELECT clause. What’s the point of creating a view when it cannot contain complex queries? In my opinion a serious RDMBS SHOULD be able to accept complex queries, hence incuding subqueries, to keep these kind of queries maintainable. Wondering though: Do the developers really under estimate the importance of these requests? Or has it actually been solved in 5.5, but did I stumble into a bug for this particular distribution? How to repeat: create view Test as select TestNumber From ( select 0 as TestNumber union all select 1 as TestNumber union all select 2 as TestNumber union all select 3 as TestNumber ) TestNumbers
[4 May 2012 17:47] Sveta Smirnova
Please do not submit the same bug more than once. An existing bug report already describes this very problem. Even if you feel that your issue is somewhat different, the resolution is likely to be the same. Because of this, we hope you add your comments to the original bug instead. Thank you for your interest in MySQL. Duplicate of bug #12755
[7 May 2012 7:18] Arjan Saly
Don’t reply patronising like this as I could NOT find the original bug report using both google and your own search engine. I did find another one, but that one was from an older version (as is the one you mention) and was not open anymore. Replies like this do not motivate me to report other bugs or feature request, given the fact that apparently your search engine does not work. Nor do I feel taken seriously as we are talking about a request that is open for 7 years already!—————————————————————————-
Bug #12755 Subquery in FROM clause of views
—————————————————————————-
[23 Aug 2005 14:12] Kay Doebl
Description: You write in your MySQL Reference Manual :: 21.2 CREATE VIEW Syntax “A view definition is subject to the following restrictions: The SELECT statement cannot contain a subquery in the FROM clause.” … Do you intend to abolish this restriction and when? We would have the advantage, not to change our code to extend our database support at MySQL. How to repeat: Mail to:
[email protected]
[4 Aug 2009 17:50] Valeriy Kravchuk
Bug #16757 was marked as a duplicate of this one.
[4 Aug 2009 17:57] Josh Duff
This bug: http://bugs.mysql.com/bug.php?id=16757&error=nd has many people requesting a fix – it really is a pain in the ass to work around. People are still posting comments on that duplicate now (it must come up higher in Google results or something). Please fix this? Pretty please?
[14 Aug 2009 20:54] HaiXin Tie
This most basic database feature has been requested by numerous users for over 5 years. A view without support of inner queries in the FROM clause can only be used as a toy, not in real world applications. This should be an essential part of any standard SQL implementation, and MySQL, though most widely used today, is the only one I know that doesn’t support it.
[17 Aug 2009 21:32] Eric Bergen
I took out the safety check and tried a few different types of queries and it seems to work fine in 5.0.27 (old I know). I think the only thing preventing this from being enabled is the check in sql_view.cc to prevent views being created on temporary tables. It just needs a way to distinguish between a sub query in the from clause and a real temporary table: /* is this table temporary and is not view? */ if (tbl->table->s->tmp_table != NO_TMP_TABLE && !tbl->view && !tbl->schema_table) {
[17 Aug 2009 21:53] HaiXin Tie
Nice!
[30 Oct 2009 21:39] Joseph Borge
This is what I have in the original 5.0.51b source: /* is this table temporary and is not view? */ if (tbl->table->s->tmp_table != NO_TMP_TABLE && !tbl->view && !tbl->schema_table) { my_error(ER_VIEW_SELECT_TMPTABLE, MYF(0), tbl->alias); res= TRUE; goto err; } I can not see the difference between Eric’s code and original code. What changes need to be made before this would work?
[7 Jun 2010 20:53] Mark Kendall
Bump, we’re investigating and attempting to add support for MySQL to a large Linux application designed for DB2. The lack of OLAP functions (specifically RANK() and DENSE_RANK()) was close to making this work not feasible but this BUG makes it a show stopper unfortunately.
[26 Mar 2011 19:45] Brian Slezak
What’s the status on this bug?
[20 Dec 2011 12:27] Arnaud Adant
You can always define another view for the subquery.
[4 May 2012 17:48] Sveta Smirnova
Bug #65185 was marked as duplicate of this one.
[7 May 2012 7:07] Arjan Saly
How about solving this bug for once? How can we ever take MySQL serious when subqueries are not allowed inviews AND this still isn’t solved 7 years (!!) after the bug has been reported?
[7 May 2012 7:10] Arjan Saly
Added a duplicate bug report because this one does NOT show up when searching either using Google or the Search engine of this site!
[2 Jul 2012 10:43] Stefan Haag
I stumbled upon this issue (again) using 5.5.21. While I see different workarounds, they are only that – workarounds. Obviously this is something coming up again and again for years. Would it be possible to have a developer commentating on this with someting more than “duplicate”? No offense. As mentioned before, the severity of this shouldn’t be S4, but more S2.
[12 Nov 2013 15:55] John Viescas
See also http://bugs.mysql.com/bug.php?id=70870. I’m happy to loudly add my voice to the clamour to have this fixed!
[9 Mar 2015 19:02] Roy Lyseng
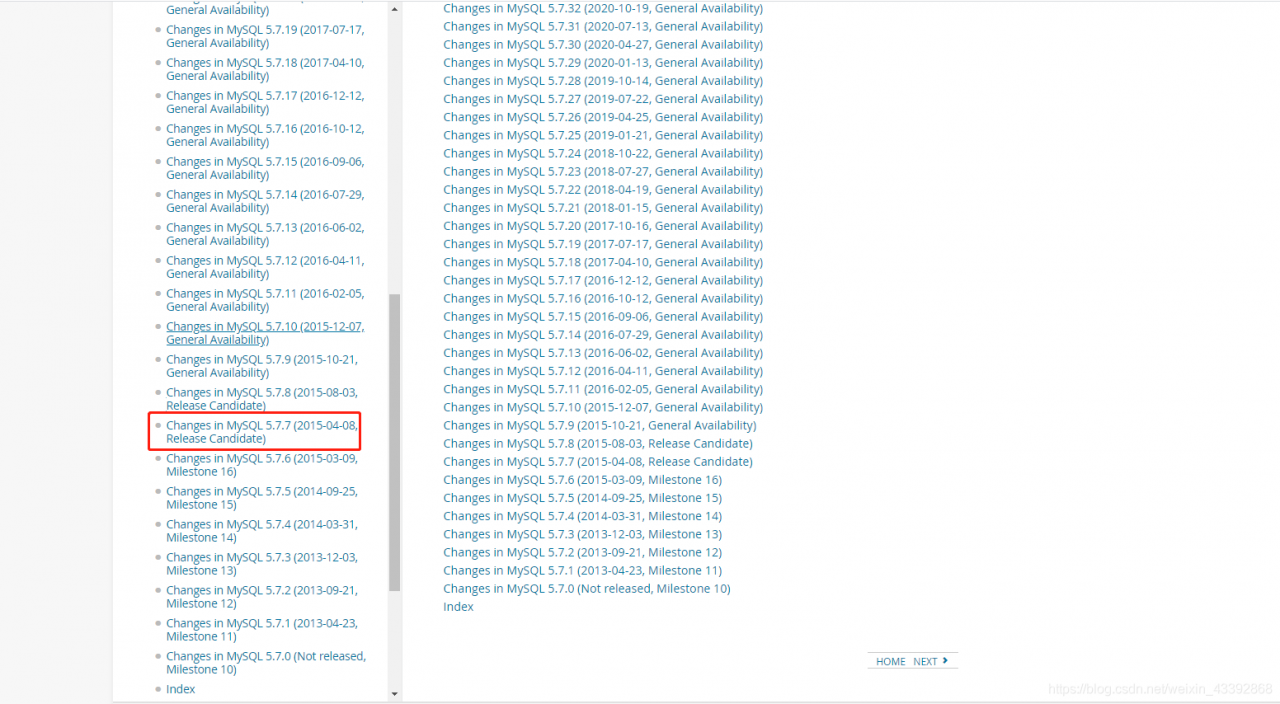
Fixed in 5.7.7
[27 Mar 2015 2:59] Paul Dubois
Noted in 5.7.7, 5.8.0 changelogs. Previously, view definitions were not permitted to contain derived tables (subqueries) in the FROM clause. This restriction has now been lifted.
—————————————————————————-
0x03 Affecting version 5.0.7 – 5.7.6
0x04 Version changelog
Find a method:
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/
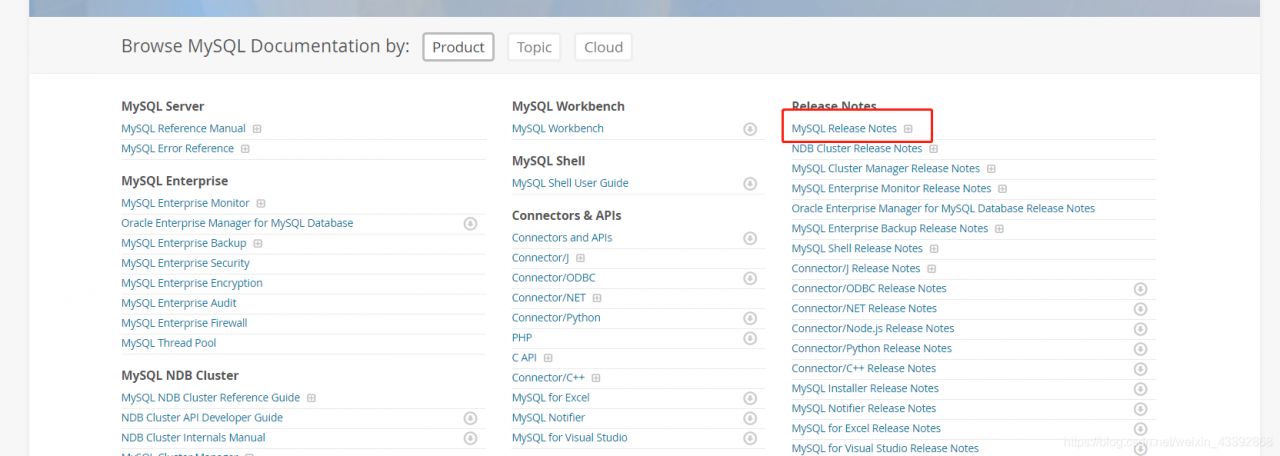
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/relnotes/mysql/5.7/en/news-5-7-7.html#mysqld-5-7-7-bug
Previously, view definitions were not permitted to contain derived tables (subqueries) in the FROM clause. This restriction has now been lifted.
Previously, derived tables (subqueries) or views in the FROM clause could not be merged into the outer query if they contained subqueries in the SELECT list. Instead, they were processed using materialization. This restriction has now been lifted so that queries previously executed using materialization can be executed more quickly using merging. (Bug #12755, Bug #11745276, Bug #60417, Bug #11865600)
0x05 Solution
(1) Upgrade mysql version to 5.7.7 and above
(2) Change the subquery to a combination of multiple views