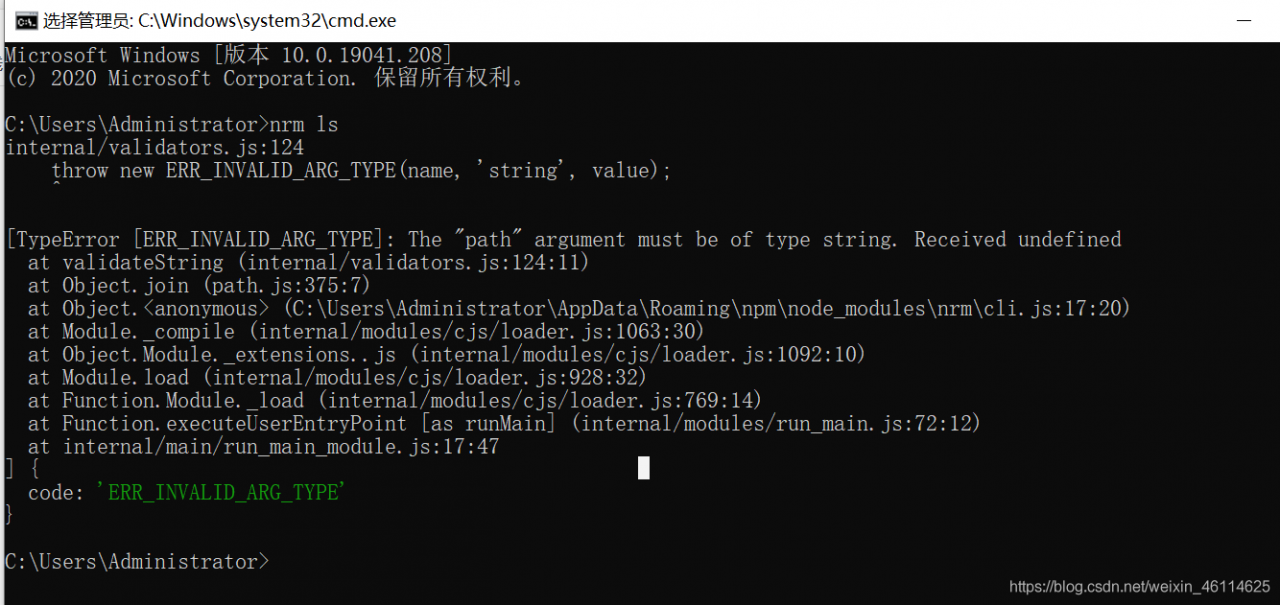
JS can use to determine whether a string contains another character
String method
1, the indexOf
IndexOf returns the position where the specified string was first found in that character. If it is not found, it returns -1
IndexOf takes two arguments. The first argument is the string to be searched and the second argument is the position to be retrieved
let str = 'abcde';
//For example, search from the third position of str 'a'
console.log(str.indexOf('a',2));// -1
console.log(str.indexOf('a'))// 0
2, lastIndexOf
LastIndexOf takes two arguments, the first is the string to be searched and the second is the position to be retrieved. The default is sting.length-1
let str = 'abcdea';
//For example, search from the third position of str 'a'
console.log(str.lastIndexOf('a',2));// 0
console.log(str.lastIndexOf('a'));// 5
3, includes
The includes() method determines whether a string contains the specified substring and returns true or false
Includes accepts two parameters, the first for the specified string and the second for the lookup location, which defaults to 0
let str = 'abcde';
console.log(str.includes('a'))//true
console.log(str.includes('a',1))//false
4, the match
g: Global search
: Ignoring case
I: The match method retrieving a specified value within a string, or finding a match of one or more regular expressions, returns null if not found (can also be used to query the number of occurrenches of a character in the string)
let str = 'abcdabcda';
console.log(str.match(/a/gi));//['a','a','a']
console.log(str.match(/z/gi));// null
5, the search
The seacrh method is used to retrieve the substring specified in the string, or to retrieve the substring that matches the regular expression, or to return -1 if none
let str = 'abcde';
console.log(str.search('a'));// 0
console.log(str.search(/A/i));//Use regular match to ignore case search Return 0
Regular expression RegExp objects
1. Test method
Retrieves the value specified in the string. Returns true or false.
let str = 'abcdef';
let reg = /A/i;
console.log(reg.test(str));// true
2. Exec method
Retrieves the value specified in the string. Returns the value found and determines its location.
Returns a matching value if there is one in the string, otherwise returns null.
let str = 'abcdef';
console.log(/a/.exec(str))// Return the matching object
console.log(/z/.exec(str))// null